Who was Lady Æthelflæd, and what do we know about her from the contemporary sources?
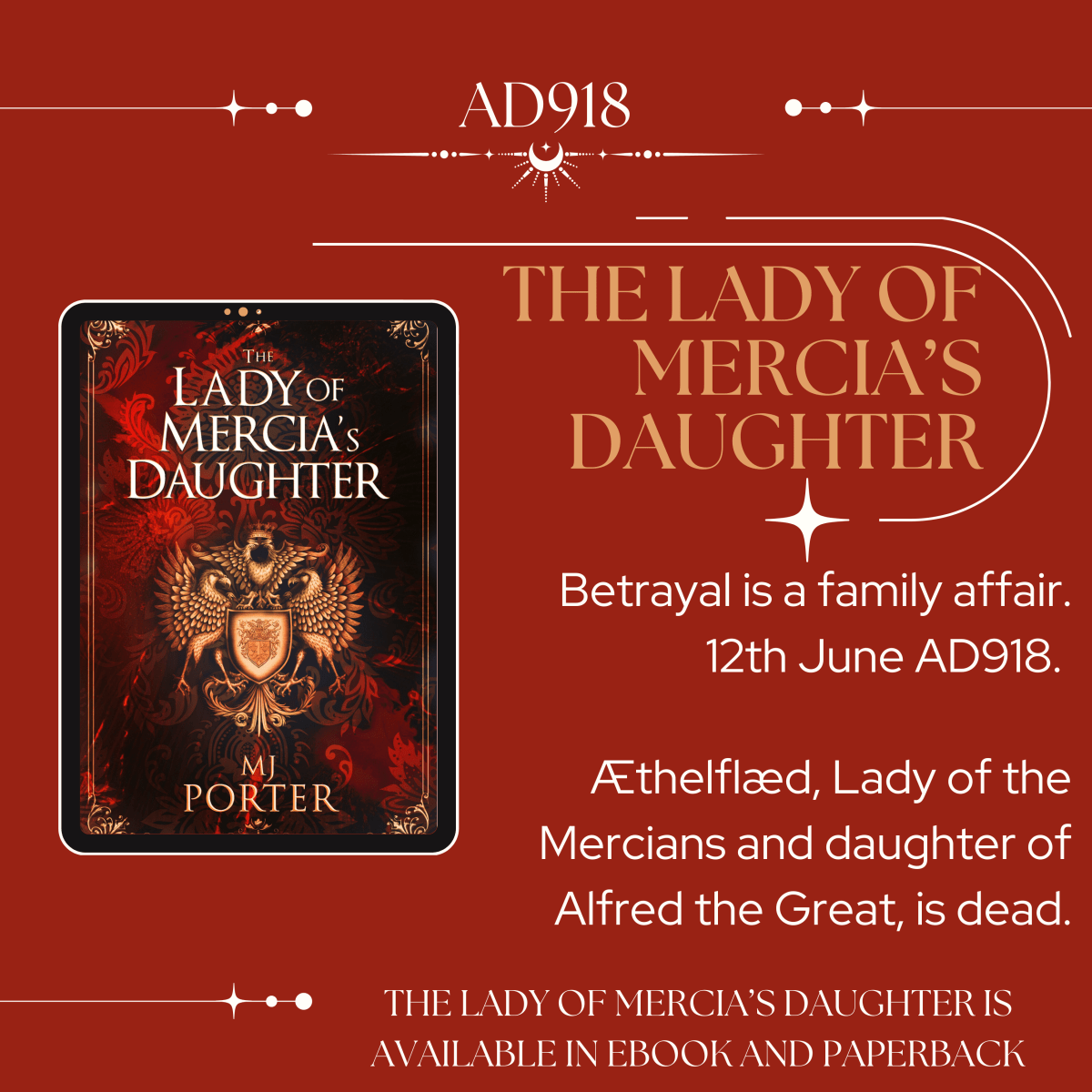
Æthelflæd,[i] said to be the oldest of the children of King Alfred, and his wife, Lady Eahlswith, was born around 866, the exact details are unknown, although the date of her death is well attested as 12 June 918.[ii]
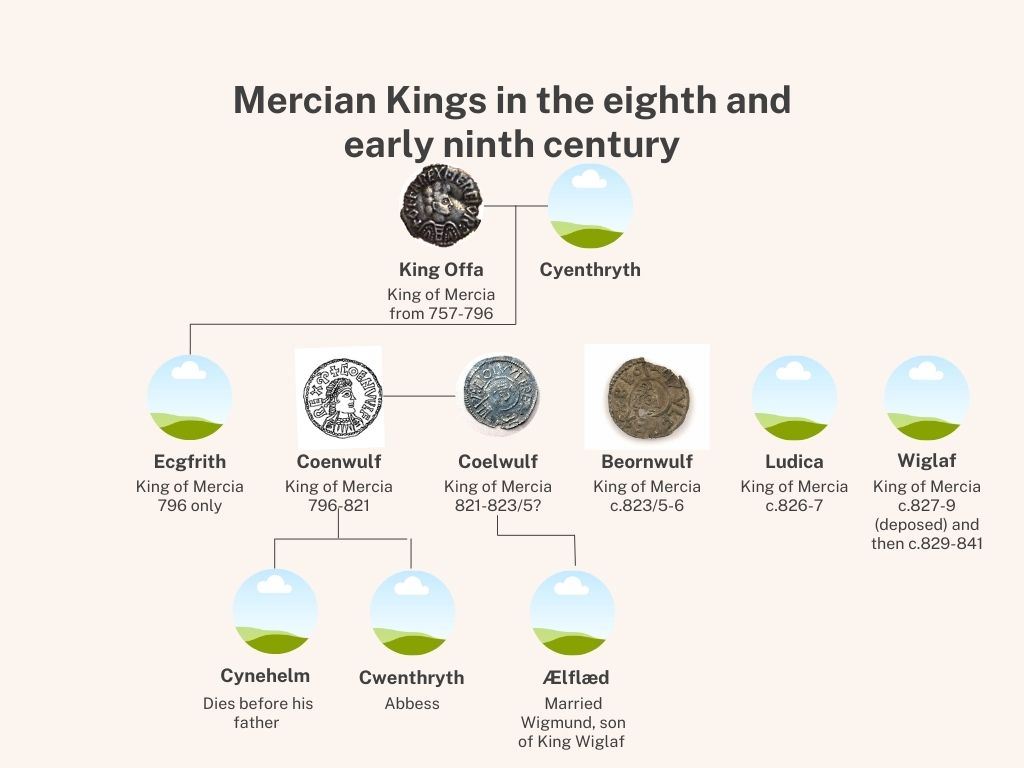
She was married to Lord Æthelred of the Mercians at some point during the 880s, although an exact date cannot be given. The first mention of this union occurs in a charter dated to 887,[iii] although the date may not be reliable. There is also little information about who Lord Æthelred might have been, and his subsequent military successes should not be dismissed, as they often are. Lord Æthelred is assumed to have been a nobleman from Mercia, and one with enough of a reputation to secure the marriage alliance with the Wessex royal family (and it must be assumed, unrelated to her mother’s birth family, and also her father’s family through his sister’s union to Burgred).
Their marriage was a success, and yet there was only one child, a daughter, Ælfwynn, born to the union, perhaps quite soon after the marriage occurred.
During her lifetime, Æthelflæd’s name appears on fifteen surviving charters. These are a real collection, some promulgated by her father, her brother, her husband and then, in her name alone. The earliest to feature her name is S223 dated to 884×9, so between 884 and 889, which survives in two manuscripts, and discussed the building of the burh at Worcester. In her final charters, she’s the sole promulgator, her husband no doubt having already died. It is believed he died in 911. S224 and S225 date to 914 and 915. S225 names Æthelflæd as the ruler of Mercia, something which The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle mirrors in some versions.
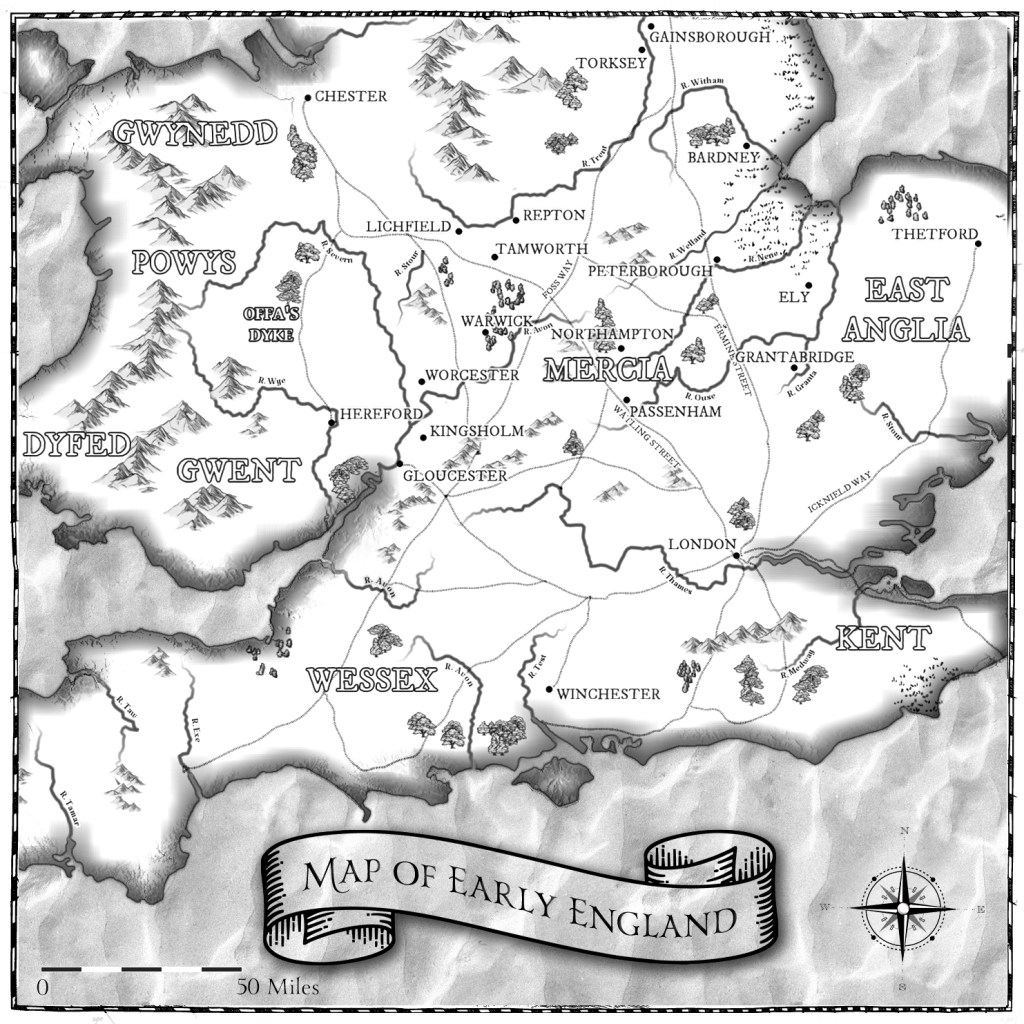
In 912, the C text records, ‘Here, on the eve of the Invention of the Holy Cross, Æthelflæd, Lady of the Mercians came to Scergeat and built a stronghold there, and the same year, that at Bridgnorth.’[xxvii]
In 913, the C text further records, ‘Here, God helping, Æthelflæd, Lady of the Mercians, went with all the Mercians to Tamworth, and then built the stronghold there early in the summer, and afterwards before Lammas that at Stafford.’[xxviii]
In 917, the C text writes, ‘Here, before Lammas, God helping, Æthelflæd, Lady of the Mercians took possession of the stronghold which is called Derby, together with all that belonged to it.’[xxxi]
Æthelflæd’s death is recorded in the A and C editions of the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle and also in the E version of the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, even if only in passing. ‘Here Æthelflæd, Lady of the Mercians, passed away.’[xxxii]
A text states: ‘and then when he (Edward) was settled in the seat there, his sister Æthelflæd at Tamworth, died 12 days before midsummer … and all the nation of the land of Mercia which was earlier subject to Æthelflæd turned to him.’
The C text of 918 offers:
Here in the early part of this year, with God’s help, she [Æthelflæd] peaceably got in her control the stronghold at Leicester and the most part of the raiding-armies that belonged to it were subjected. And also the York-folk had promised her – and some of them granted so by pledge, some confirmed with oaths – that they would be at her disposition. But very quickly after they had done that, she departed, twelve days before midsummer, inside Tamworth, the eighth year that she held control of Mercia, with rightful lordship; and her body lies inside Gloucester in the east side-chapel of St Peter’s Church.[xxxiii]
It seems highly probable that Æthelflæd’s death, when it came, was unexpected, occurring in the middle of an advance into the Danelaw and the Five Boroughs (Derby, Nottingham, Lincoln, Stamford, Leicester). It was left to her daughter, and also her brother, to continue her work, and you can read their story in The Lady of Mercia’s Daughter and A Conspiracy of Kings.
Or you can read about the historical women in my non-fiction title, The Royal Women Who Made England.
You can can read all about her daughter, the historical Ælfwynn here.

[i] PASE Æthelflæd (4)
[ii] Swanton, M. ed. and trans. The Anglo-Saxon Chronicles, (Orion Publishing Group, 2000), AD 918
[iii] S217, surviving in two manuscripts
[xviii] Baker, N. and Holt, R. ‘The city of Worcester in the tenth century’, in St Oswald of Worcester: Life and InfluenceBrooks, N. and Cubitt, C. ed, (Leicester University Press, 1996), pp.134–5
[xix] Sawyer, P.H. (ed.), Anglo-Saxon charters: An annotated list and bibliography, rev. Kelly, S.E., Rushforth, R., (2022). http://www.esawyer.org.uk/, S1446
[xxi] Sawyer, P.H. (ed.), Anglo-Saxon charters: An annotated list and bibliography, rev. Kelly, S.E., Rushforth, R., (2022). http://www.esawyer.org.uk/, S1282
[xxii] Hart, C.R. The Early Charters of Northern England and the North Midlands (Leicester University Press, 1975), p.102 (100)
[xxvi] Swanton, M. ed. and trans. The Anglo-Saxon Chronicles, (Orion Publishing Group, 2000) Ibid., p.94
[xxvii] Ibid., p.96
[xxviii] Ibid., p.96
[xxix] Ibid., p.97
[xxx] Ibid., p.100
[xxxi] Ibid., p.101
[xxxii] Ibid., p.103
[xxxiii] Ibid., p.105
[xxxv] See Stafford, P. After Alfred. Anglo-Saxon Chronicles and Chroniclers 900–1150, (Oxford University Press, 2020), for a full discussion of the Æthelflæd and Edward Chronicles.