(I’m re-sharing an old post which I’ve amended slightly, and added some new graphics).
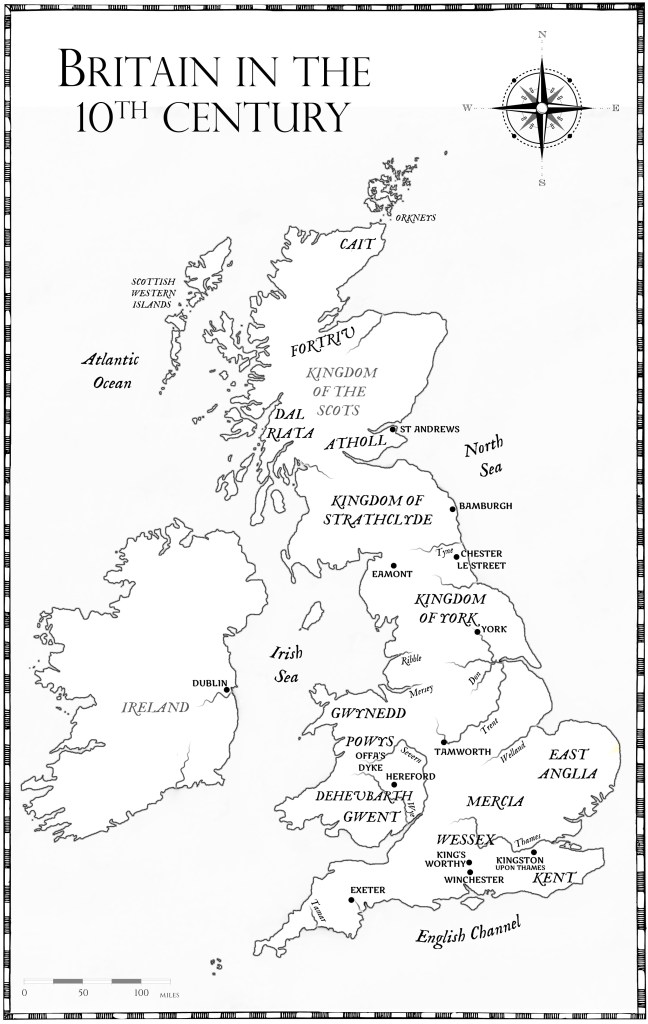
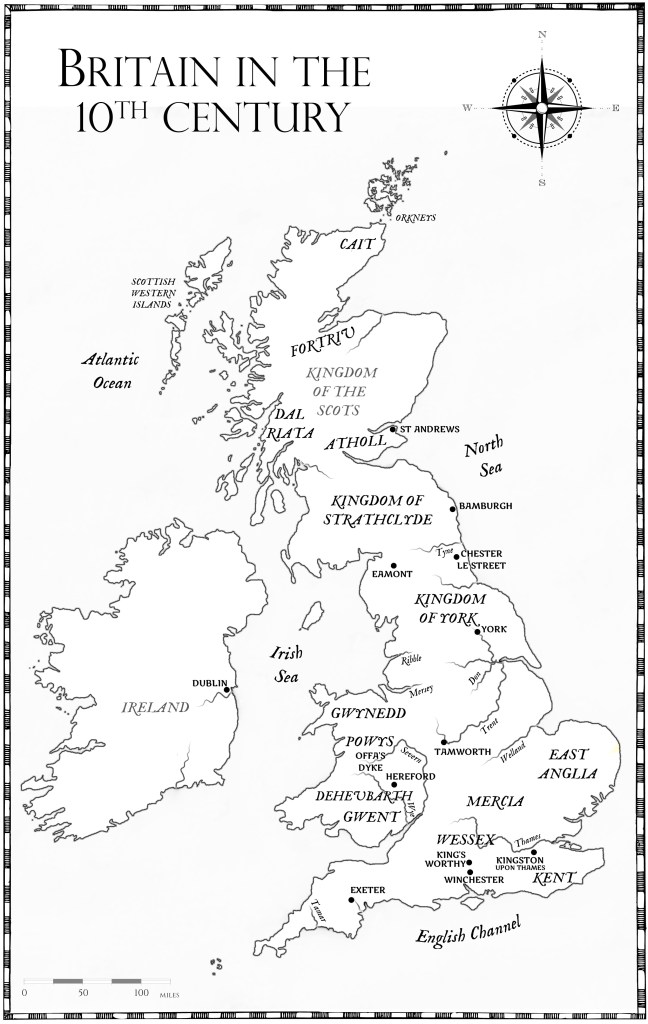
England, Wales, Scotland, the smaller kingdoms of Mercia, Wessex, Northumbria, East Anglia, Kent, Powys, Gwynedd, Dal Riada – for the uninitiated (including myself) the sheer number of kingdoms and kings that peopled the period in British history before 1066 can appear as a bewildering display of names, places, times and events, and perhaps never more so than when a historian is trying to sell a book and so makes a statement in their title that applies to that particular king.
Phrases such ‘the Golden Age of Northumbria’, ‘the Mercian hegemony’, ‘the rise of Wessex’, they all mask so many events that I find the phrases very unhelpful and perhaps worse, misleading.
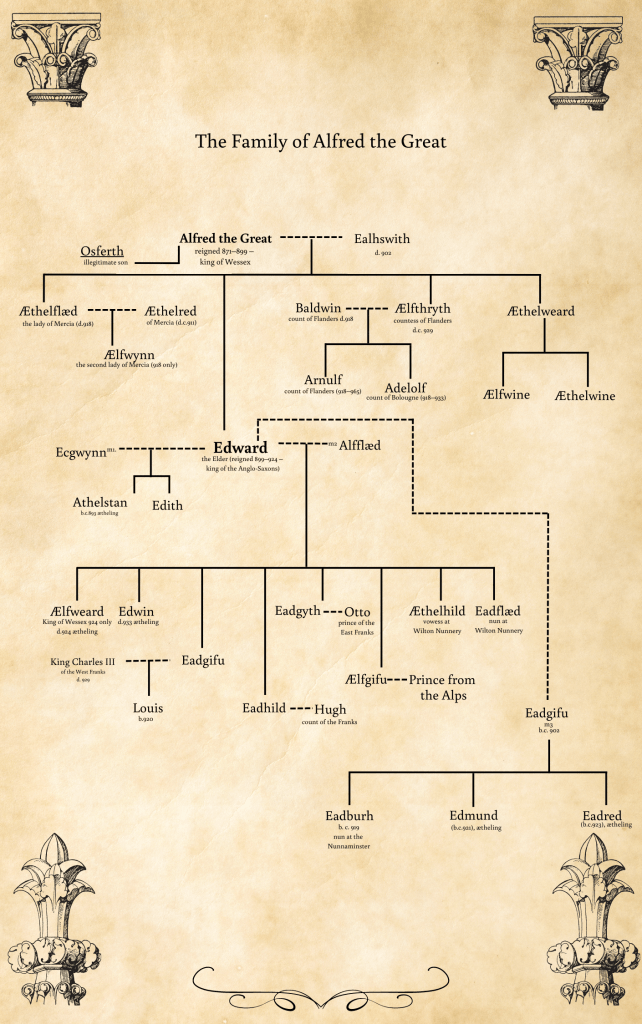
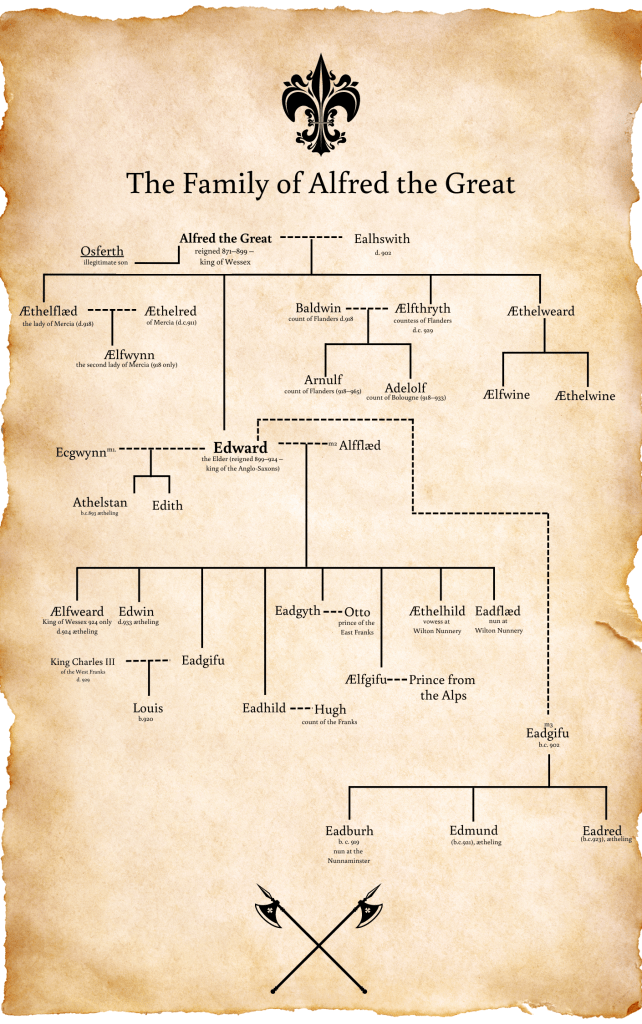
I think that Athelstan and his younger half brother, Edmund, probably deserve their titles as Kings of the English. And it’s not just my opinion either. There was, according to Sarah Foot in her book on Athelstan, a concerted effort by the king and his bishops to have him stand apart from his predecessors – to be something ‘different’ to them. They named him king of the English, not king of Mercia (a post he held briefly before another of his younger brothers died) and not king of Wessex, for all that he was both of those things.
They changed his title, they crowned him with a crown, not a helmet. They wanted Athelstan to be something other than his grandfather, King Alfred, and his father, King Edward. It was a bold statement to make, and one they continued when Athelstan died too young and his half-brother, Edmund replaced him. He too was crowned using, it must be supposed, the same Coronation service. (For full details have a peek at Sarah Foot’s book on Athelstan – or read the first few chapters of King of Kings as the service appears in it as well).
So why the change? Essentially the old Saxon kingdoms, for all that they were preserved in the naming of the earls/ealdormens designations, had been swept aside by the Viking raiders. The old kingdoms had become a handy label to apply to certain geographic areas, and the kings of Wessex, whilst keen to hold onto their hereditary titles because of the permanence their own royal line had managed to acquire, were equally as keen to do away with regional boundaries. There was, it can’t be denied, a concerted and almost unrelenting urge to drive any Viking raider or Dane or Norwegian (the Norse) from British soil, and this is what Athelstan and then Edmund were tasked with doing.
Yet the idea of ‘English’ wasn’t a new concept. Why else would Bede have called his great piece of religious historical writing “The Ecclesiastical History of the English people’, if there hadn’t been a shared consciousness that the people in England, all be it in their separate kingdoms, didn’t have a shared heritage? Why the idea suddenly took flight under King Athelstan could be attributed to a new sense of confidence in Wessex and Mercia at the time. They were confident that they could beat the Viking raiders and they were convinced that England belonged to them.
Or perhaps it was more than that? The destruction wrought by the Viking raiders on the separate kingdoms must have been a stark reminder of just how insular the kingdoms had become, and the Viking raiders showed everyone just how easy it was to run roughshod over the individual kingdoms. Only in unity could the Saxon kingdoms of England survive another onslaught; only with unity could the Saxons hold onto their kingdoms they’d claimed about 500 years before.
It was a message that was learned quickly and taken to heart. Athelstan worked to reunite more of the Saxon kingdoms with the growing ‘England’, and he tried to do so by both diplomacy and through war. Yet, the Viking raiders hadn’t finished with England, and nor were they her only enemies. This also lies at the heart of Athelstan’s ‘masterplan’ his treaty of Eamont (if it truly happened – Benjamin Hudson in his Celtic Scotland is not convinced). Athelstan wanted to be a mighty king, but he also wanted England, and the wider Britain (also a concept already understood otherwise why else would that cantankerous monk – Gildas – have called his even earlier work than Bede’s “On the Ruin of Britain?”) to be united in their attempts to repel the Viking raiders. He was a man with a keen vision of the future and it was a vision that his brother continued, with slightly different direction and results.
The ‘English Kings” saw safety in unity, and of course, an increase in the power they held went hand-in-hand with that.
Yet at no point during the Saxon period can it be said that the emergence of ‘England’ as we know it, was a given certainty. Throughout the period other great kings had tried to claim sovereignty over other kingdoms, but never with any permanence. The earlier, regional kings, were powerful within their own lifetimes and within their own regions. Few, if any, were able to pass on their patrimony complete upon their death. This was a time of personal kingship, and it was only under Athelstan and Edmund that the leap was taken away from this to a more permanent power base.
Not that it was a smooth transition and it did have the side-effect of allowing other men, those not related to the royal family, to evolve their own individual power bases in the old Saxon kingdoms. The ‘English’ kings had to do more than just rule their own kingdom, they had to rule their ealdormen and earls, their warriors, bishops and archbishops. The number of names of kings might start to deplete in the after math of Athelstan and Edmund’s kingship, but in their place spring up more and more powerful men, men that these English kings had to rely on.
Becoming King of the English was very much a mixed blessing, bringing with it new and greater responsibilities and more, it brought with it the need to expand personal government further, to have a greater persona to broadcast.
King of Kings is available now, and Kings of War is coming in July 2023.