Welcome to my release day post for Protector of Mercia. I’m going to talk about the kings who preceded all the chaos of the series.
Readers of the Eagle of Mercia Chronicles will have encountered the names of kings Coenwulf and Coelwulf, although the kings in the first book, Son of Mercia, ruled after both Coenwulf and Coelwulf. But, having written about Coelwulf II in the Mercian Ninth Century books – which feature an older, and wiser Icel, I was eager to return to an equally unsettled period in Mercia’s history. And this, helped by the fact that Icel would just have been old enough at this period to be involved, very much helped set the scene. However, the aftermath of the reigns of these two men, brothers, are very much at the heart of political affairs during the Eagle of Mercia Chronicles.
So, who were Coenwulf and Coelwulf or Ceolwulf?
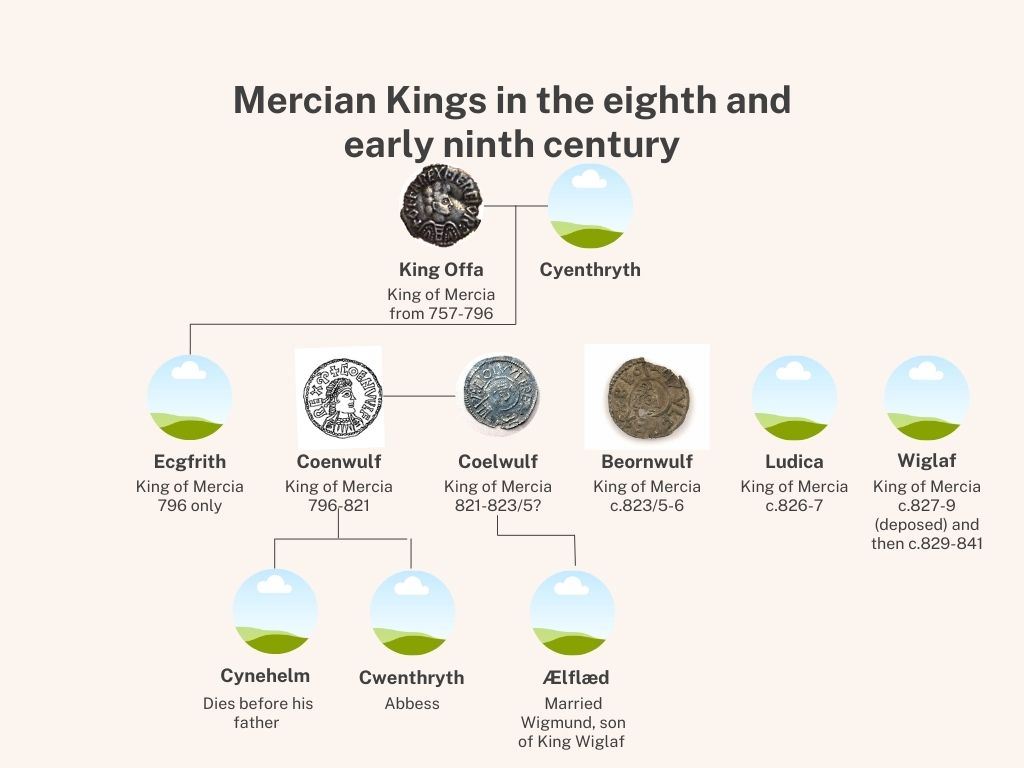
Coenwulf, the first and only of his name, was king of Mercia from 796 until his death in 821. He claimed descent, not from the previous king Offa (of Offa’s Dyke fame), and his son, but instead from Pybba, who is believed to have been the father of both Kings Penda and Eowa (read about them in my Gods and Kings trilogy) who ruled in the seventh century. You might have heard of Penda. Although the connection isn’t sound, he is often referenced when talking about the Staffordshire Hoard.
It does seem as though the crisis of the late 820s/830s and the slow decline of Mercian power have overshadowed all that King Coenwulf achieved, not helped by the fact that his son, who was to succeed him, died before his father (if he existed at all), so that on Coenwulf’s death, the kingship passed to his brother, Coelwulf, and he in turn was overthrown at some point in 823-826. The brother kings seem to have shared another brother as well, who may have been king of Kent, after Mercia annexed the kingdom to its own domain.
But Coenwulf was a successful ruler. He claimed the kingship after the death of Offa’s son, Ecgfrith, not long after his father’s death, (Offa is said to have been keen to eliminate all rivals to the kingship which is why, when his son died, the kingship had to pass to a more obscure branch of the ruling line), and while he suffered reverses in Kent and the kingdom of the East Angles, he does seem to have exercised control in both places, and was also aggressive against the Welsh kingdoms throughout his reign. Mercia, at this time, was NOT confined to the current English Midlands, it was a much vaster kingdom although it’s firm boundaries are difficult to establish.
While the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle is sparse about our brother kings, that didn’t stop the later Norman writers, embellishing the story of them. But first, what do we hear about these kings from the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle?
‘Ceolwulf, king of Mercia, ravaged over the inhabitants of Kent as far as the Marsh, and [they] captured Præn, their king, and led him bound into Mercia.’ 796 [798[ (A)
´Here Coenwulf, king of Mercia, passed away, and Coelwulf succeeded to the kingdom.’ 819 [821] (A)
´Here Ceolwulf was deprived of his kingdom.’ 821 [823] (A)
´And the same year King Egbert and King Beornwulf fought at Ellendynm and Egbert took the victory; and a great slaughter was made there…. And that year the East Angles killed Beornwulf, king of the Mercians.’ 823 [825[ (A)
´Here Ludeca, king of Mercia, was killed, and his 5 ealdormen with him, and Wiglaf succeeded to the kingdom.’ 825 [827] (A)
´Here Wiglaf obtained the kingdom of Mercia again.’ 828 [830] (A)
Henry of Huntingdon, one of the Anglo-Norman author, writes of Cenwulf, our Coenwulf
‘Not long afterwards, Cenwulf, king of Mercia, beating and ravaging his way through the Kentish province, captured their king Præn, who could not match his strength and was lurking in the coverts and isolated places, and victoriously took him back in chains.’ p.259
Coenwulf’s brother, Coelwulf, succeeded him, but not for long, until he was usurped. Henry of Huntingdon in summarising affairs in Mercia adds.
‘Cenwulf reigned peacefully for twenty-six years, and died the common death.
Ceolwulf possessed the kingdom for three years, which the fierce Beornwulf then wrested from him.’ p.271
The Chronicle of John of Worcester adds similar details.
‘[821] Ceolwulf, king of the Mercians, was driven from his kingdom, and Beornwulf was raised to the kingship.’p241
There is some confusion regarding children born to either brother, and indeed, much that is known of that later Coelwulf II stems from the fact he shared a name with one of the two brothers, and as such, his connection with that ruling family can be supposed by experts in the field (not me). It appears that Coenwulf had a son and a daughter, the daughter well known as an abbess at a local nunnery, and possibly, two wives. King Coelwulf is known to have had one daughter, Ælflæd, who married Wigmund, the son of King Wiglaf. But there is a distinct lack of information regarding these individuals. We don’t know when the usurped King Coelwulf died. We don’t know when his daughter died, for certain, and obviously, other children are unknown.
The Chronicle of John of Worcester, another Anglo-Norman writer, informs us that.
‘[819] St Cenwulf, king of the Mercians, after a life devoted to good deeds, passed over to the eternal blessedness which is in heaven, and left his 7-year-old son St Kenelm heir of his realm. But when a few months had passed, by the treachery of his own sister Cwenthryth, whose cruel spirit had been roused by an awful lust for power, he was secretly done to death with cruel outrage by Æscberht, his most bloodthirsty tutor, in the shade of a thorn tree in a deserted wood. But he who was slain with heaven alone as witness, was later revealed by heaven’s witness through a column of light. Kenelm’s head was cut off, milk-white in the beauty and innocence of birth, and from it a milky dove with golden wings soared to heaven. After his happy martyrdom, Ceolwulf received the kingdom of the Mercians.’ P239-241
Henry of Huntington adds. ‘At Winchcombe you will read of the secret martyrdom of Kenelm. He was the son of Cenwulf, the Mercia king, who died in the year of grace 819, having reigned for twenty-four years. The martyrdom of his son Kenelm was revealed from heaven to Pope Silvester II at Rome.’p691
However, Coenwulf and Coelwulf I do seem to have enjoyed military successes. Coelwulf’s attacks on Wales are mentioned in the Annales Cambriae.
‘818 Cenwulf [Coenwulf] devastated the Dyfed regio.
822 The fortress of Degannwy is destroyed by the Saxons and they took the kingdom of Powys into their own control.’ p48
The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle is not helpful about the reigns of either brother, other than referencing their accession and either death or deposing. We don’t know the date that Coelwulf I died, although he clearly lived after being deposed.
Increasingly, scholarship is looking at Mercia during this period – if the answers can’t be found in the surviving written sources they can be found elsewhere. When King Alfred began his revival in education, many of the scholars he turned to were Mercians, highlighting Mercia’s accomplishments in all spheres – and the correlation has been made that the same happened in Mercia after the end of Northumbria’s Golden Age. There is also a wealth of Mercian sculpture dated to this period which hints at the power and influence of the kingdom, perhaps even of artistic centres at the heart of certain designs.
This doesn’t yet help us truly appreciate the power these kings could wield – so often overshadowed by what happened after their reigns, but it certainly shows we should be wary of accepting this absence in the written sources as indicative of their failure. Indeed, we should be wary of any Wessex-centred source from later in the same century (the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle) that might not only suffer from Wessex-bias, but may also reveal a desire to overshadow Mercia in order to proclaim Wessex’s kings as the more powerful. This is something that is certainly at the heart of the revival in interest in the descendant of these two kings, King Coelwulf II, or Mercia’s last king, written about as a ‘foolish king’s thegn’ in the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle but clearly very far from being that.
It’s intriguing to realise that our Norman writers only had access to much the same information that we do in order to offer an account of what was happening in Mercia at this time. But they do seem to have enjoyed embellishing the words of the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, and while arguments are often made that they may have had access to local sources not written about in the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, especially for John of Worcester, who wrote at one of the most important Mercian centres, until their words can be entirely unpicked, we must be wary of using their additions as historical ‘fact,’ in much the same way that we need to be wary of the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle(s).
Quotations are taken from the following translations. Darlington, R.R. & McGurk, P. ed. The Chronicle of John of Worcester Volume II The Annals from 450 to 1066(Clarendon Press, 1995). Greenway, D. ed. and trans. Historia Anglorum, The History of the English People, Henry of Huntingdon, (Clarendon Press, 1996. Morris’ translation of Nennius and the Welsh Annals and Swanton’s The Anglo-Saxon Chronicles.
Protector of Mercia is released TODAY.
books2read.com/protectorofmercia
If you’ve not yet started The Eagle of Mercia Chronicles, then check out this introduction to the series.
Sign up to my monthly newsletter to learn more about my writing journey, new releases and special offers, and receive a free short story collection featuring many stories of Saxon England.
Discover more from MJ Porter
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.






One thought on “Kings of Mercia in the early ninth century – the brother kings, Coenwulf and Coelwulf/Ceolwulf”