Here’s the blurb
Witness the rise of the Tudors in the stunning conclusion to Conn Iggulden’s powerful retelling of the Wars of the Roses.
‘An utterly compelling page-turner full of historical facts. A fascinating read’ Sun
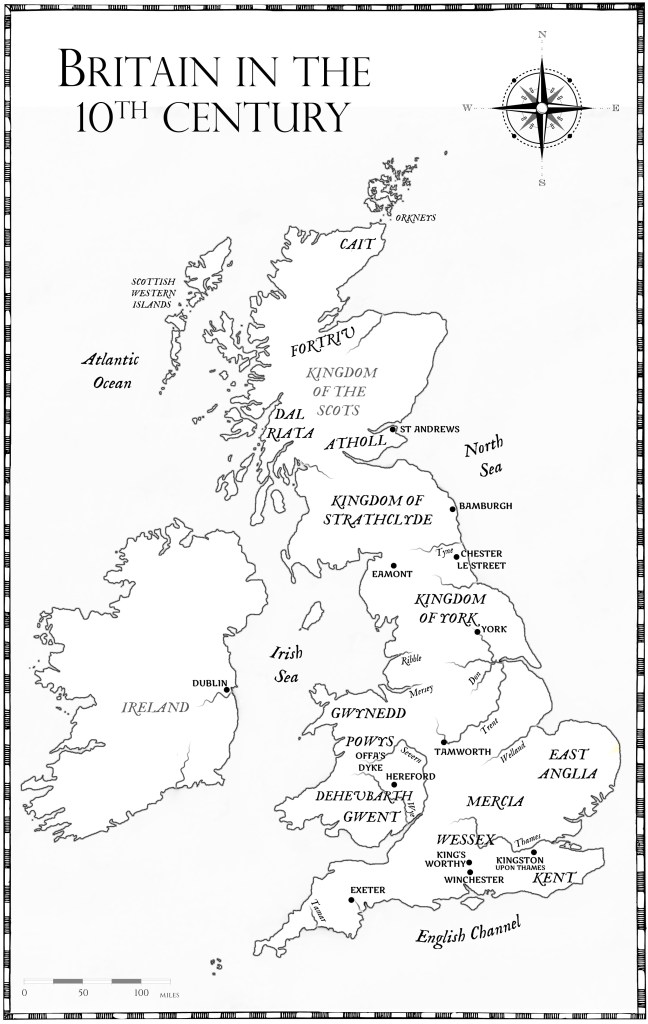
England, 1470. A divided kingdom cannot stand.
King Edward of York has been driven out of England. Queen Elizabeth and her children tremble in sanctuary at Westminster Abbey. The House of Lancaster has won the crown, but York will not go quietly.
Desperate to reclaim his throne, Edward lands at Ravenspur with a half-drowned army and his brother Richard at his side. Every hand is against them, every city gate is shut, yet the brothers York go on the attack.
But neither sees that their true enemy is Henry Tudor, now grown into a man. As the Red Dragon – ‘the man of destiny’ – his claim to the throne leads to Bosworth Field and a battle that will call an end to the Wars of the Roses . . .
My Review
Ravenspur, by Conn Iggulden, the fourth book in a series about the Rise of the Tudors, suffers, from the very beginning, with pacing issues and an apparent unease from the author to actually tell the story of the battles of the War of the Roses, even though this novel ‘hooks’ itself onto the important battles of the period, ending with the Battle of Bosworth Field. The author goes to a great deal of trouble to set up each and every battle, and the reader is left wanting greater details of the battle, only for the author to almost gloss over the entire thing and move onto the next chapter in the long-running civil war.
Furthermore, the desire of the author to get to the Battle of Bosworth in this novel means that the novel is uneven – 80% of the novel takes place over the space of a single year, and to all intents and purposes, looks as though it will stop there, only for it to leap forward eleven or twelve years and continue telling its story. It would perhaps have been better to split this novel into two books and allow Richard III a little more time on the throne.
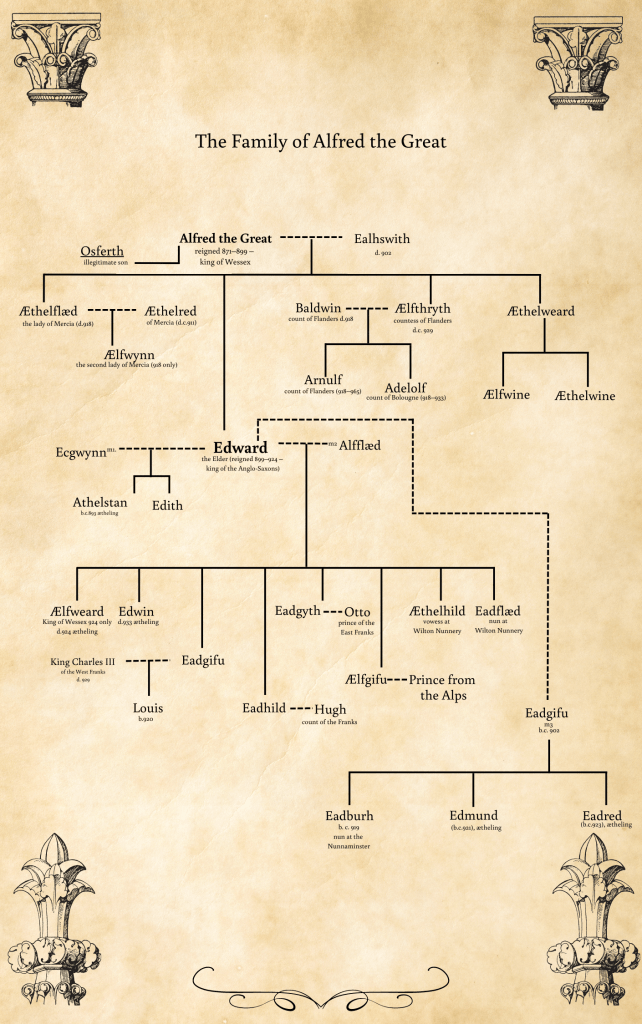
The characters of the period are told with little flare and with absolutely no sympathy for their plight. The main women in the story – Margaret of Anjou and Elizabeth Woodville barely have any pages to themselves and when they do appear it is more often that not only as objects for the male characters of the story to complain about or belittle. And this continues with Richard III’s poor wife.
The male characters of the story are equally presented with little or no understanding of their characters and not a single one of them elicited any sort of emotional response. Edward IV is a swaggering idiot (and fat for quite a bit of it), Earl Warwick is indecisive and stupid, Richard III (or Gloucester) is a simpleton following his brother where ever he takes him and then turning into some sort of possessed maniac, and poor old Edward, son of Margaret of Anjou, just gets to look pretty and make a fool of himself in battle.
Overall, the story moves very slowly, and without any emotional connection with the characters, it is a slog to get to the end, which many will already know. And that’s another problem. With good historical fiction, even the inevitable conclusion is often presented as only one possible outcome, with this novel there is never any (apart from briefly before the Battle of Barnet) moment where I wondered if the author had managed to present a possible alternative, which would ultimately fail, but would still give a little bit of hope to the reader and the characters in the story both. Sadly, I was disappointed with such a drab retelling of the end of the War of the Roses.