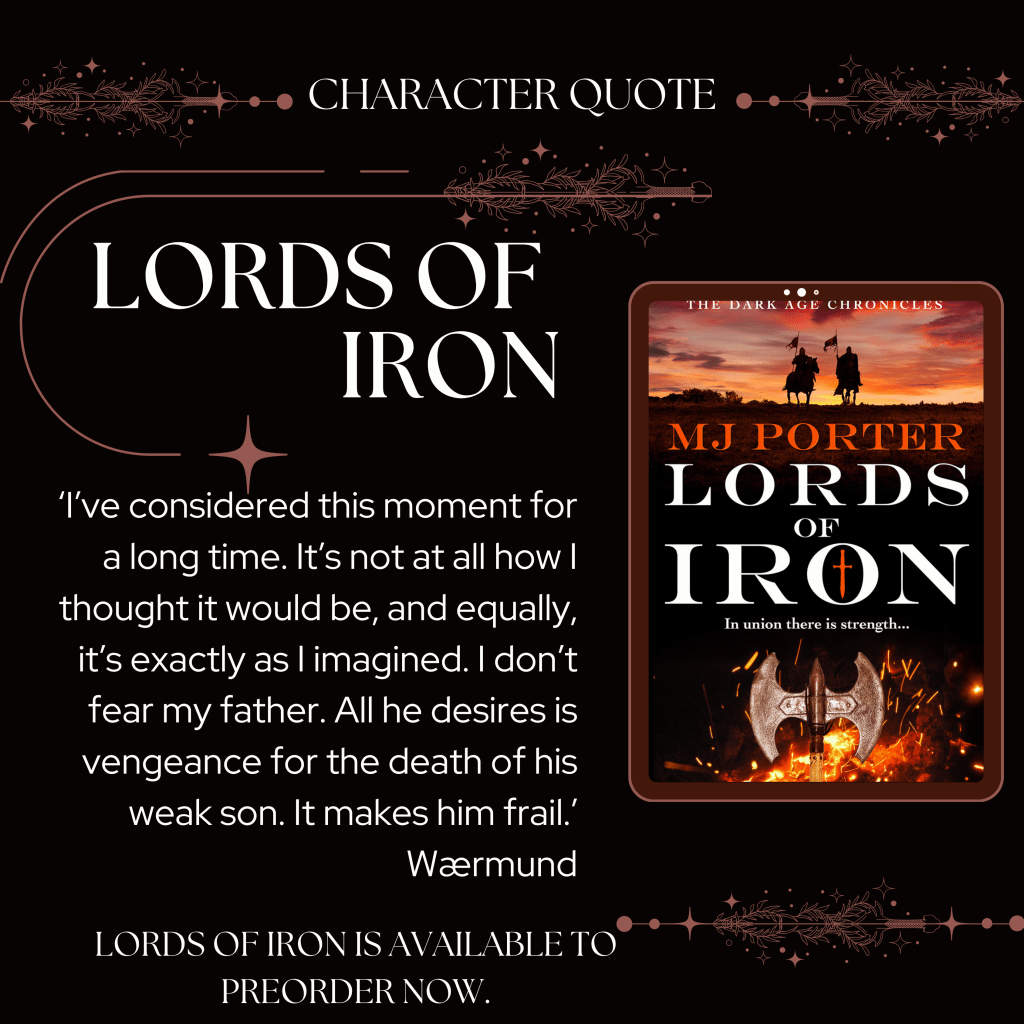
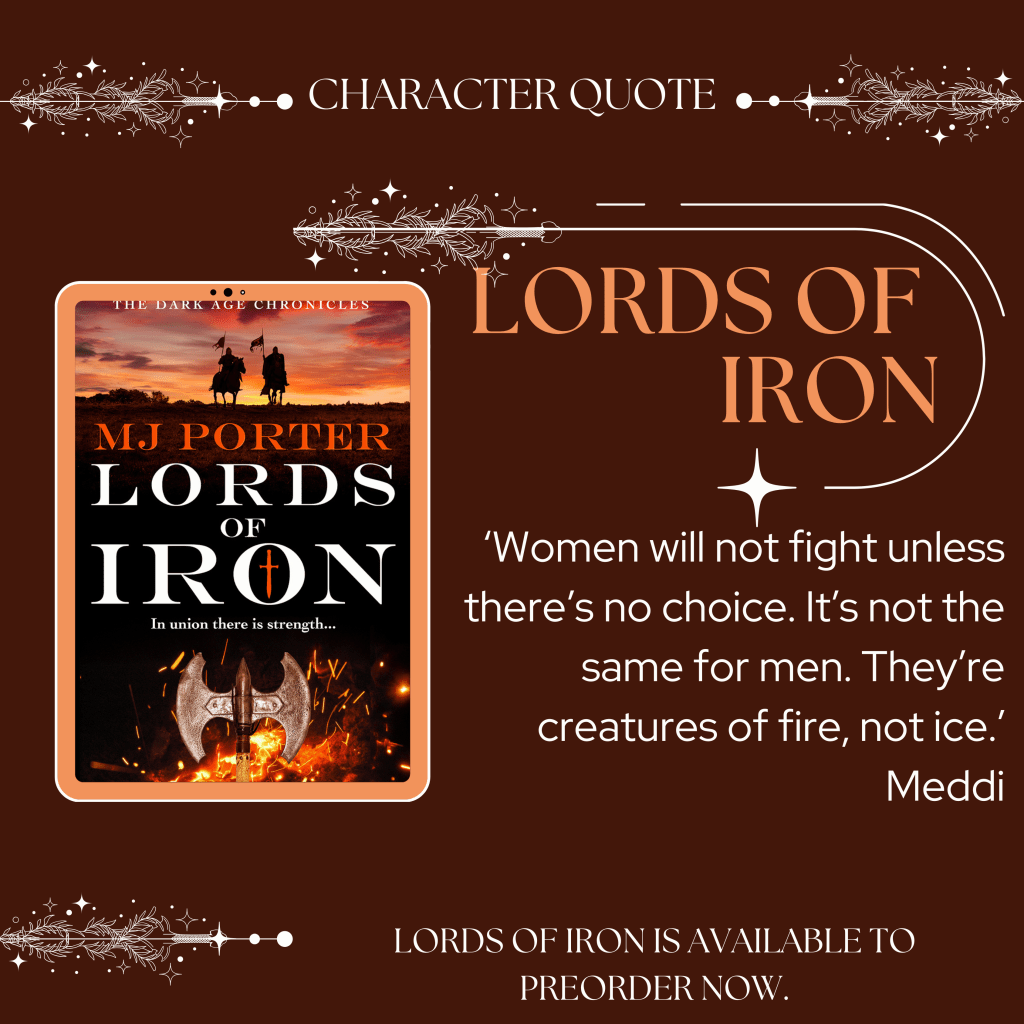
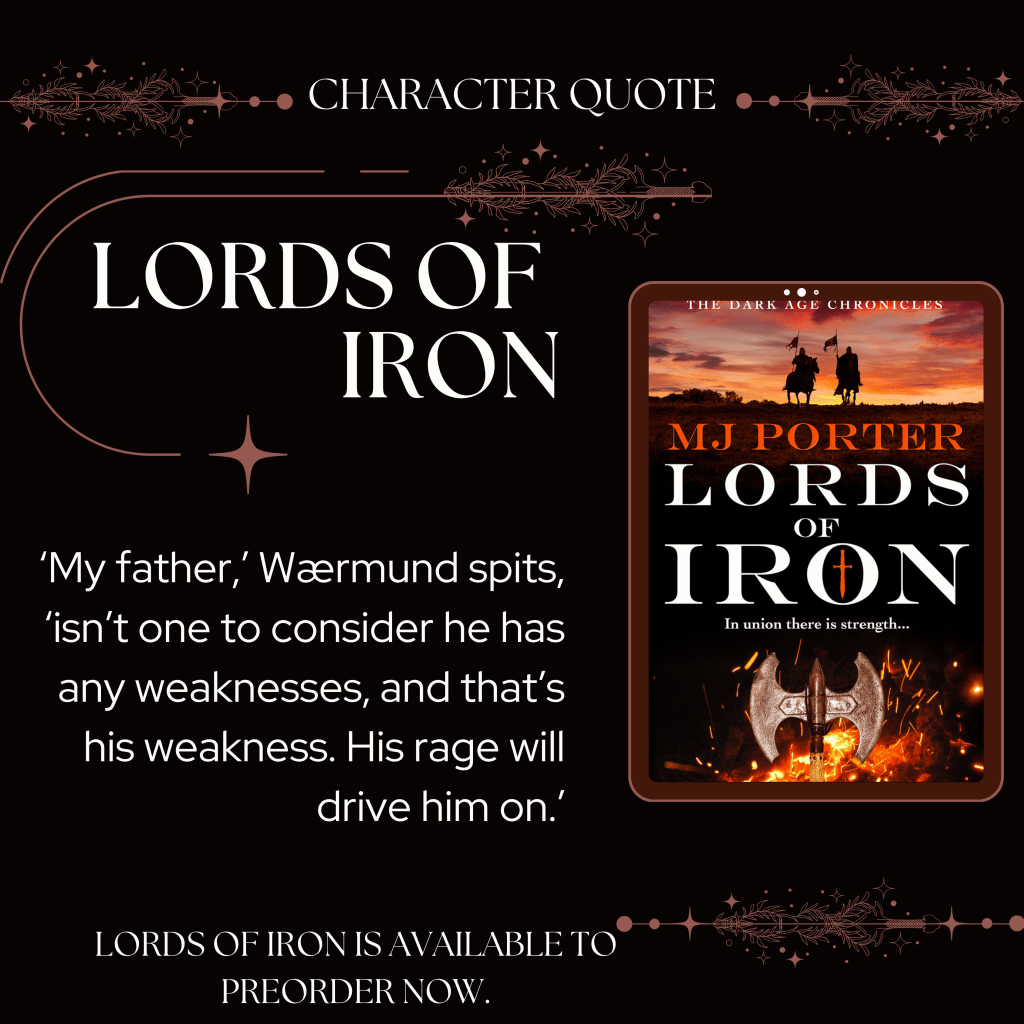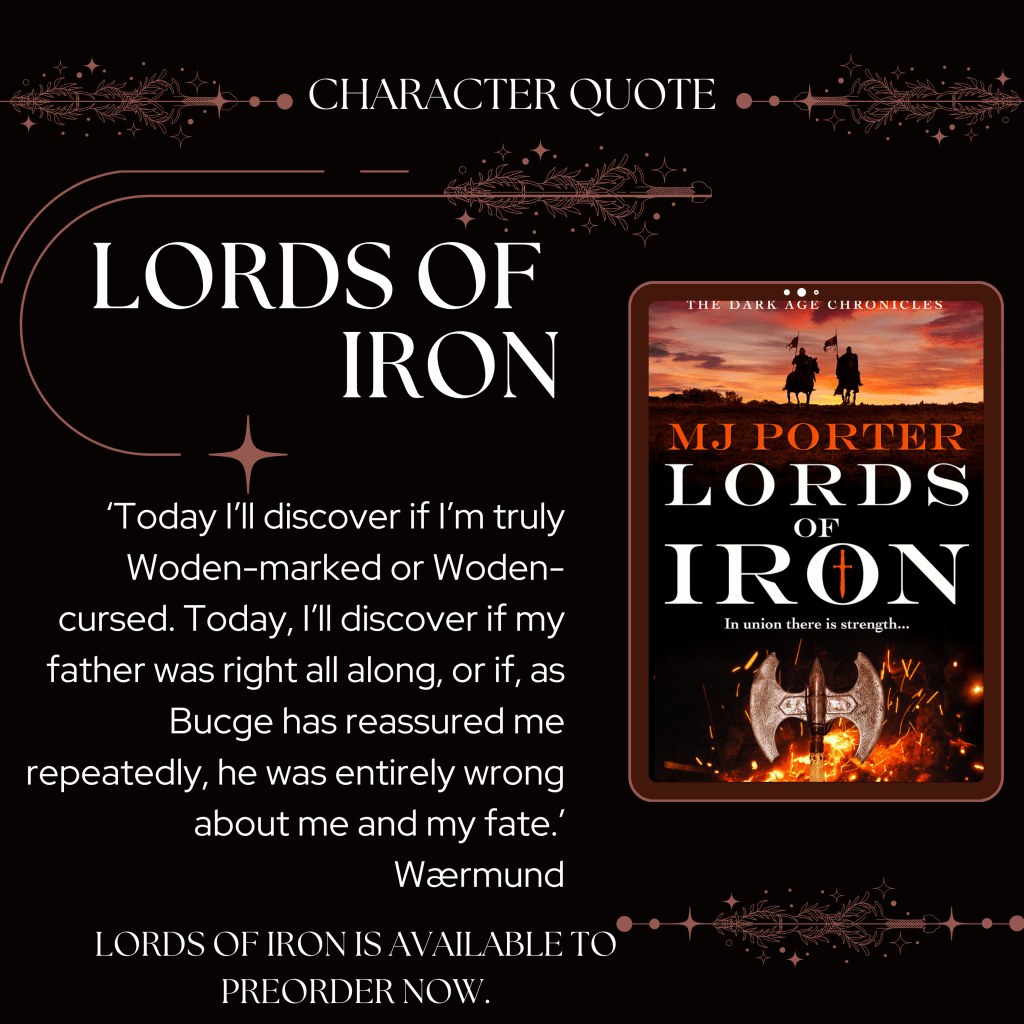What comes after the events of the Dark Age Chronicles (as well as before)
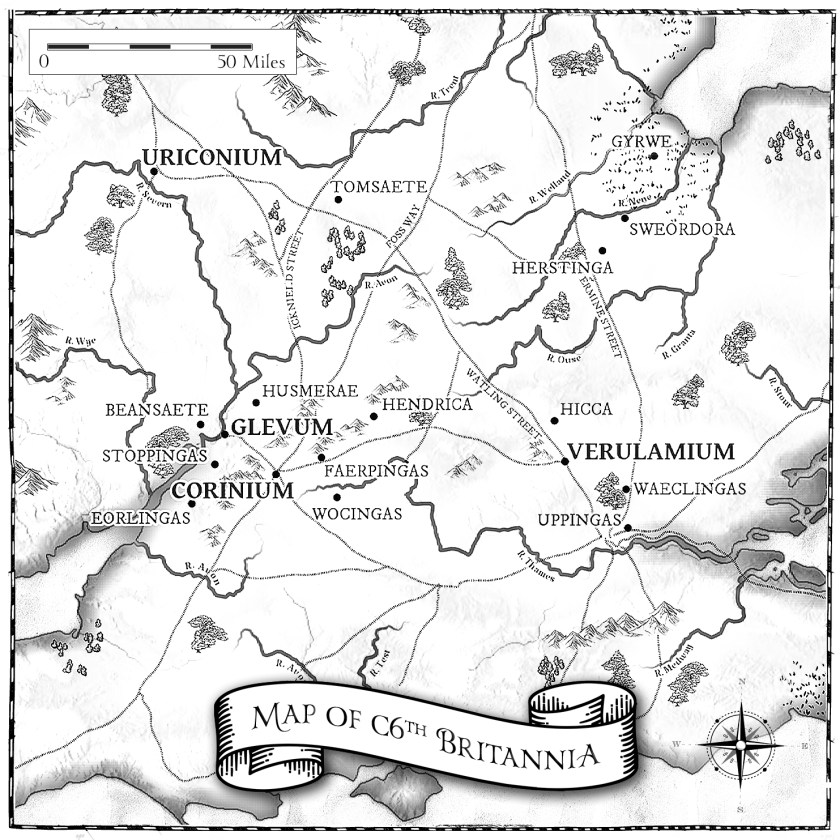
In deciding on a date to set the Dark Age Chronicles, I was quite careful. I wanted it to be after the era of the legendary Arthur (the battle of Camlann is dated to 537 in the Annals Cambriae (the Welsh Annals)), but also before written sources start to make some references to what was happening in what would become Saxon England in the later 500s anywhere that wasn’t in the south/south-east.
In the A version of the ASC there are 26 entries for the 500s. Eight are dated before AD540. These are mostly concerned with events in the south, Kent, the Isle of Wight, and Portsmouth, and their legendary Saxon founders. After 540, we’re treated to the genealogies for what would become Northumbria (547 and 560), Wessex (552 and 597) as well as having references to the religions in Britain at the time, through accounts of Columba and the missionary activities in Kent from Pope Gregory. There are any number of battles between those forging a foothold in their newly forming kingdoms and the native Britons.
Our first real reference for anything happening in what would become the kingdom of Mercia is under the year 577 when we’re told Gloucester, Cirencester and Bath were taken from the ‘Britons’ by Cuthwine and Ceawlin (of Wessex). Gloucester would certainly be within the later kingdom of Mercia. Cirencester and Bath weren’t.
While I’ll repeat that the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle wasn’t begun until the 890s (so over 300 years later) and Bede, which much of the ASC is based on at this time, was writing in the 730s (so nearly two hundred years later), I still wanted almost a clean slate for my characters to inhabit. There was also the matter of plague to try and avoid, as well as a series of bad harvests, that are referenced but don’t form more than a background detail in the books.
I felt that to truly gain a ‘feel’ and an ‘understanding’ for what might have been happening at this time, it was necessary to step aside from any historical account and to rely on the archaeological record. The years 540 and 541 felt as though they provided a good opportunity to do just that. However, it’s always important to have an eye to what was going to happen, as well as what had happened before. And, as I wrote, a number of elements seemed to become very clear to me. While there are reports of battles amongst the Saxon invaders and the native populations (six of them in those eight entries before 540, although some of them are quite small), and while they feel quite overwhelming when simply listed because they form so much of the narrative, there aren’t a lot of them mentioned before AD540. The impetus certainly seems to gather pace after that date (of the remaining 18 entries, eight reference what seem to be quite large battles). Why this might have been, began to make sense as I explored the idea of no new iron production after the end of Roman Britain, until the skill was ‘rediscovered.’ Without the ability to easily overwhelm an enemy through new blades that weren’t made from recycled metals, would people who’d endured famine and plague, really want to risk it all when there was no chance of success? It felt unlikely. Would you? The need to fight isn’t always taken when you know you’ll succeed, sometimes it’s also desperation, but if these settlements were doing reasonably well, why take the chance? Surely, they needed to rebuild and form alliances to survive.
And so, as I’ve written the trilogy, what would come after – the increasing battles, the desire of the invaders to establish ‘kingships’ in Wessex, Kent, Northumbria, Mercia and the kingdom of the East Angles, began to make a lot more sense – with the rediscovery of how to forge sharpened blades (or indeed, to import them when the ‘invaders’ arrived (whether to intermarry or to make war), because unlike in Britannia, the ability to forge blades didn’t become lost in the homelands of the Saxon invaders) there were suddenly people who could start to dominate, and who would want to dominate.
And yet, the archaeology couldn’t be forgotten either. There aren’t many battle sites known from this era. What can be said with more surety, is that there was a co-mingling – all sorts of crossovers are found in the burial record – and indeed, the burial rites of many changed during this undocumented sixth century. There was undoubtedly discord between peoples, but there was also accord. Until there wasn’t. So, something had to change to bring about the formation of the Saxon kingdoms. I’m not saying my ideas are correct, but they are intriguing, especially when played out in a fictional environment where I can endeavour to explain what might have been happening – both in terms of war, and peace. (And, some would argue not all iron production was lost – it certainly wasn’t – but it becomes much more difficult to ‘find’ – i.e. no nails to secure coffins in the burial record in the heartland of England – what was happening in Wales/Devon and Cornwall is very different).
After the Dark Age Chronicles, we move into a period where identifiable kingships and kingdoms are forming – we’re moving into what would become Saxon England, and towards the events of the seventh century, which would be dominated by discord between Mercia and Northumbria, Wessex and the other kingdoms, and the reigns of the alleged ‘bretwaldas’ (wide rulers.) We’re moving towards what’s more immediately understood and known, but the sixth century is where these developments have their routes, as twisted, tangled, unexplainable and often, as baffling as they are. (And we don’t really need a legendary figure to explain what’s happening, do we, although the prevalence of Excalibur does perhaps answer to these questions as well?). We’re moving towards The Gods and Kings Trilogy.
Purchase Link



Check out the Dark Age Chronicles page for more information about the trilogy
Blog links

Posts
Stay up to date with the latest from the blog.