I write about the Saxon kingdom of Mercia a lot. I thought it had been entirely unintentional until now. But has it?
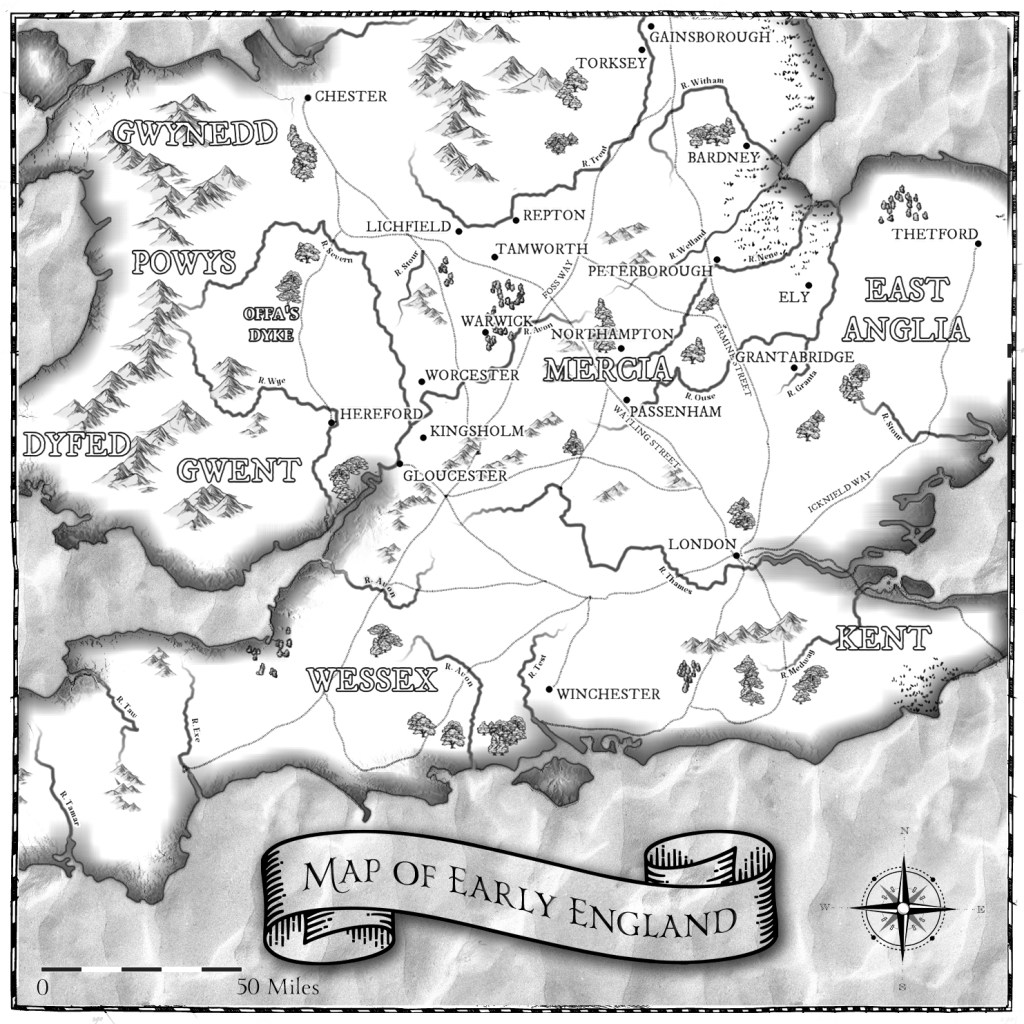
I grew up in an area that would one have been in Mercia. From a seemingly young age, I knew Mercia had once been a kingdom in its own right. I knew I lived in the centre of what had once been a mighty kingdom. The local church’s name, St Chad’s, was a dedication to a priest who converted the Mercians to Christianity. Tamworth, the next city along, was also a capital of Mercia (and where much of the Son of Mercia is set). Repton, a little further afield, a Mercian royal mausoleum, so when I went to university and began to study the period, I was, of course, drawn to that kingdom, to Mercia and to all it could offer me.
The Early English kingdom of Mercia is unfortunate in having no extant records surviving from the height of its power and reach. Northumbria has the works of the Venerable Bede and his Ecclesiastical History of the English People. Wessex has the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle (ASC) – a collection of nine extant ‘versions’ of the same chronicle but with some later regional bias. Mercia has none of these things – although one of the ASC’s may be more Mercian in tone than others. Mercia also has a collection of surviving charters, and also many, many sculptures, that can be dated to this era.
It’s believed that any Mercian annalistic records that existed were destroyed by the Raider Viking attacks that gained in intensity throughout the ninth century. This is highly possible. It means that we never truly ‘hear’ the story of Mercia. We hear a Northumbrian view of Mercia. And we hear a Wessex view on Mercia. What of Mercia itself? We also hear views of Mercia from Alcuin and his collection of letters from the later eighth century.
Students of Early England are taught very much in a set chronological pattern of the Golden Age of Northumbria in the seventh century, the Supremacy of Mercia in the eighth and then the slow but seemingly unstoppable expansion of Wessex to claim all of England under one kingship so that by the time we reach 1066, England as we know it today, exists and is ruled by one king. This glosses over the fact that these kingdoms all existed simultaneously. They all fought and argued amongst one another. They all had ambitions to rule much more of modern England than their kingdom borders necessitated.
And, of course, the joy of redressing the balance a little is never far from my mind. I aim to make sure that people know of Mercia and don’t just think of its growth, supremacy and decline, as though the kingdoms of Northumbria and Wessex were more to blame for what befell Mercia than its own kings and inhabitants.
And so Mercia? What of Mercia during the Golden Age of Northumbria (the Gods and Kings trilogy)? What of Mercia through the decline of its supremacy (the Eagle of Mercia Chronicles), through the Viking Raider attacks and the growth of Wessex (the Mercian Ninth Century), after the death of Lady Æthelflæd (the Lady of Mercia’s Daughter) and what happened to Mercia during the final one hundred years of Saxon England (The Earls of Mercia series)?
What indeed? It’s not a small task, but it’s one I’ve set myself. And I’m far from finished with it. I have plans for more new titles, in time.
Check out the series pages
The Eagle of Mercia Chronicles
Discover more from MJ Porter
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.