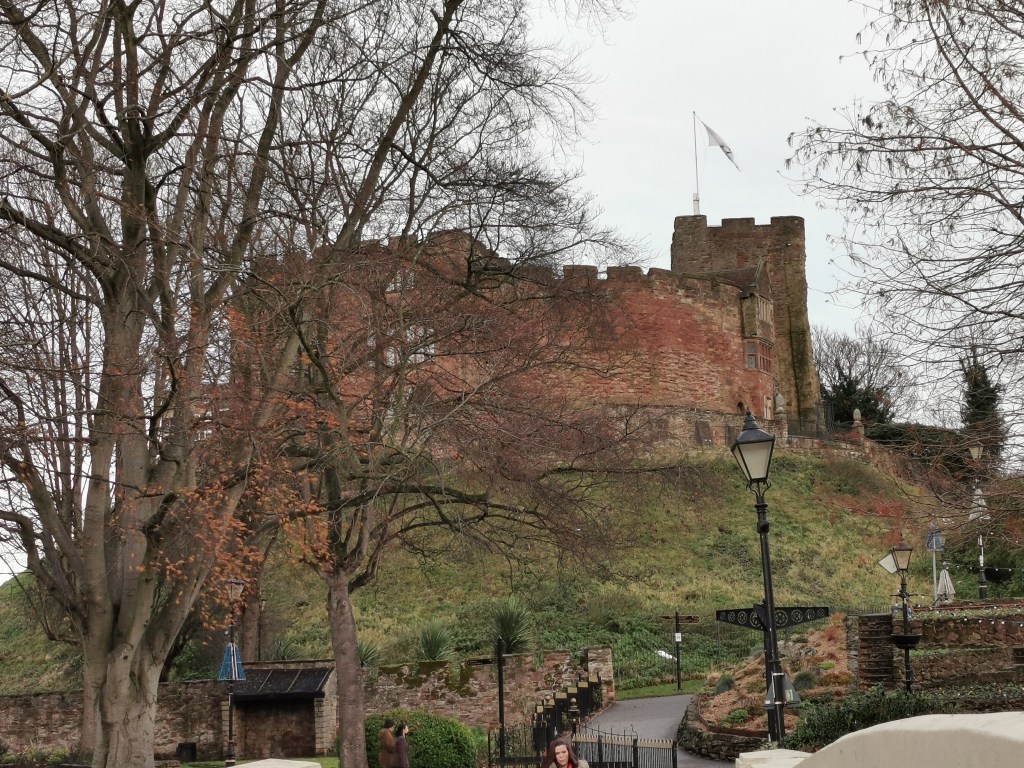
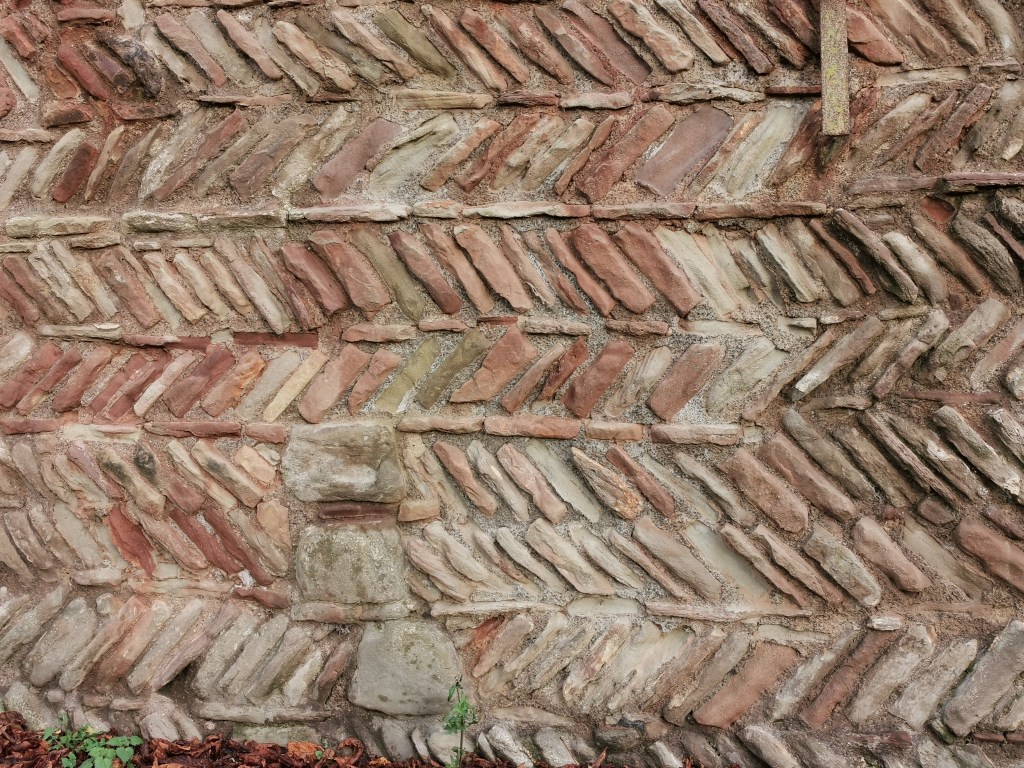
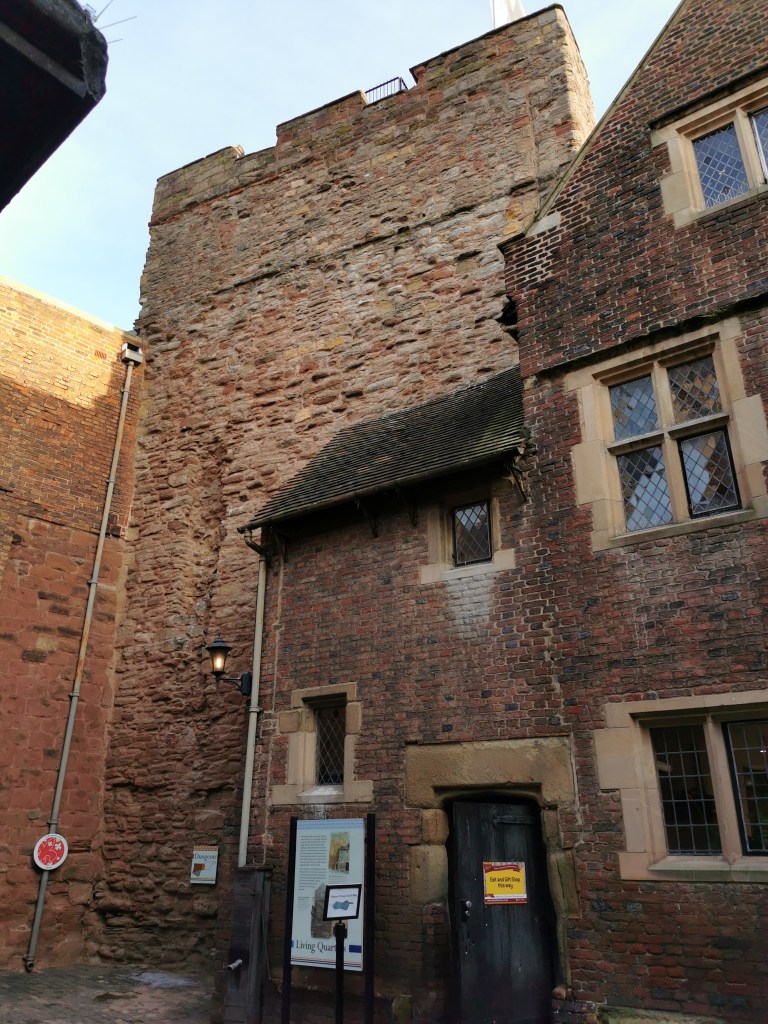
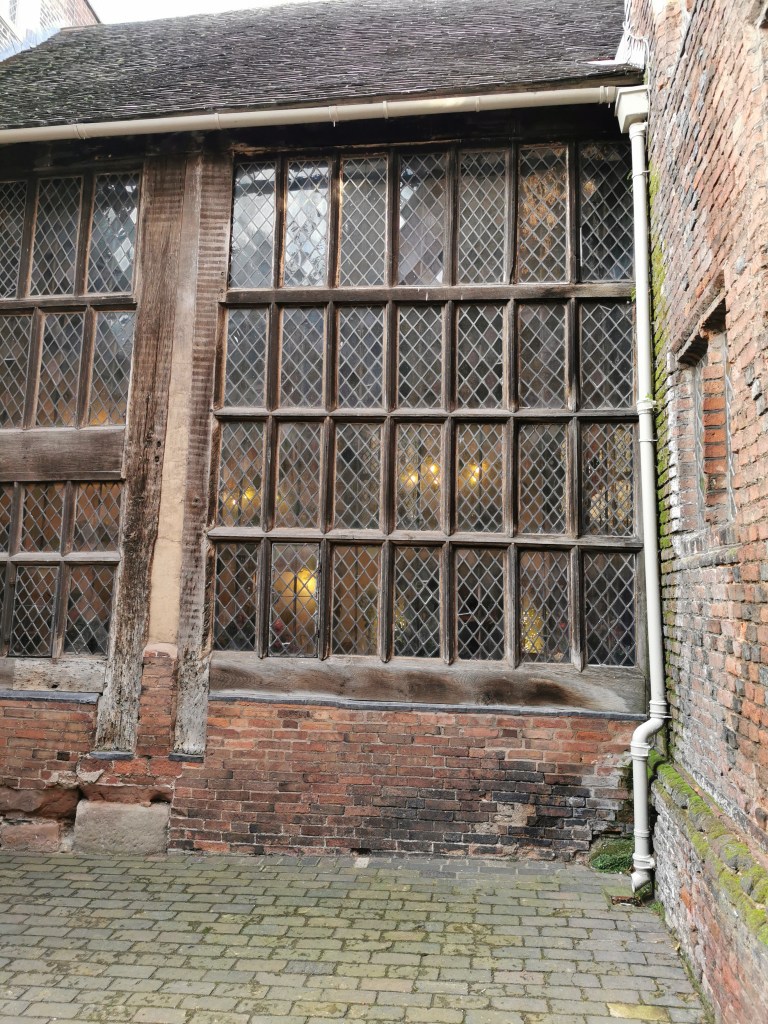
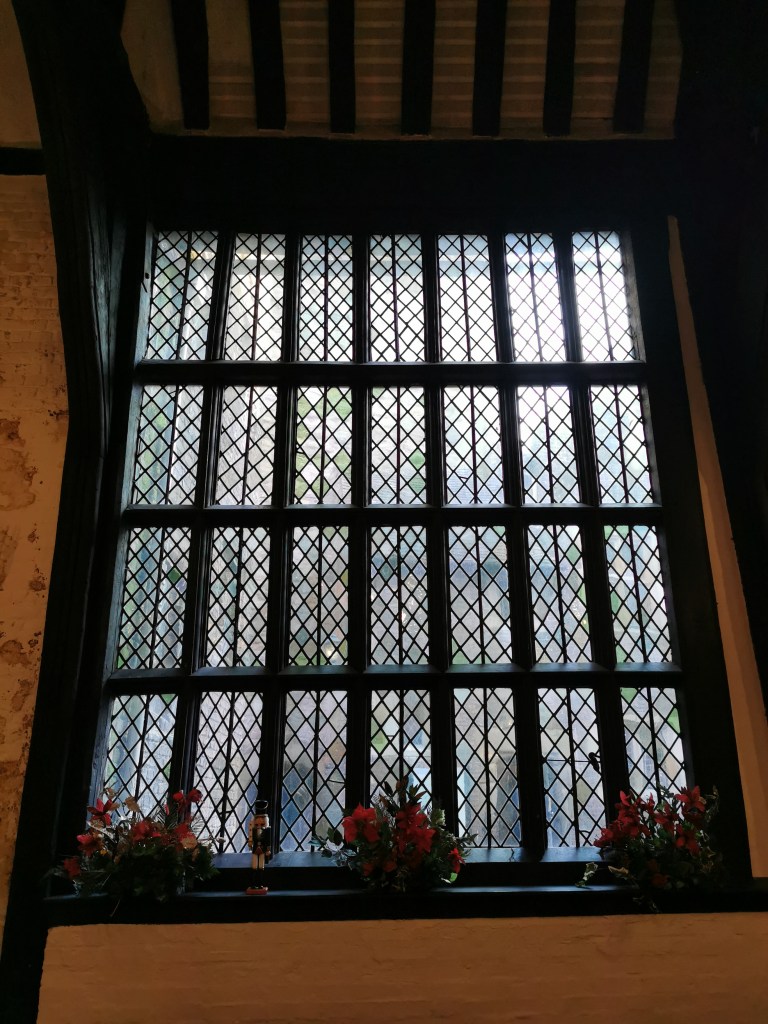
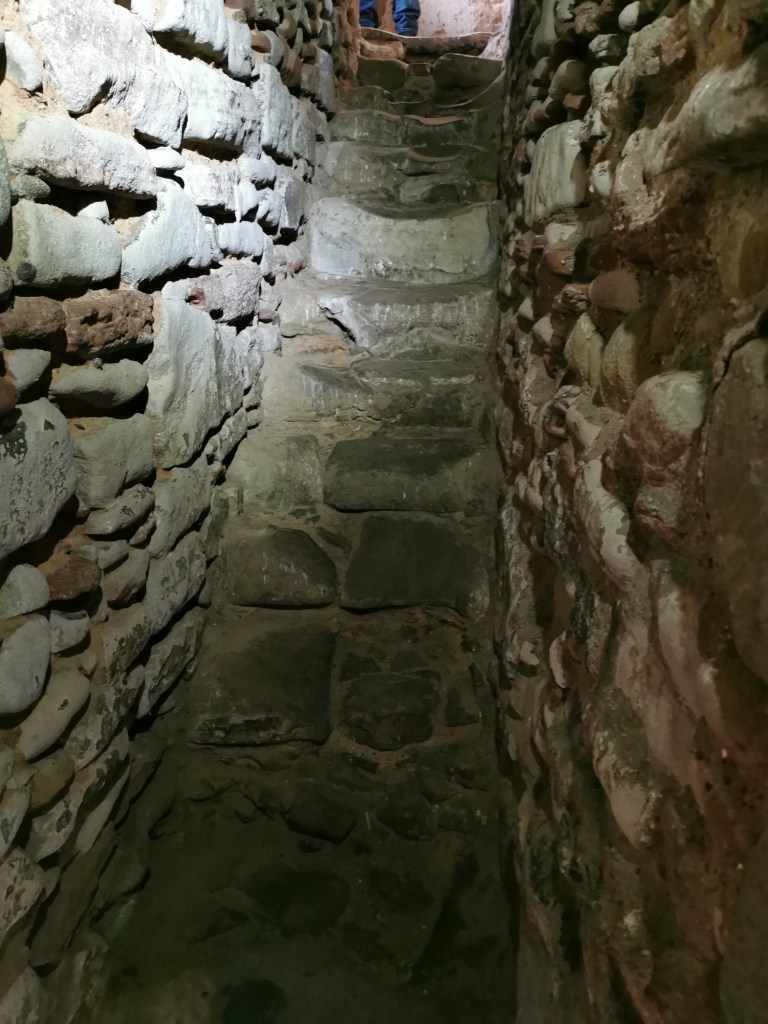
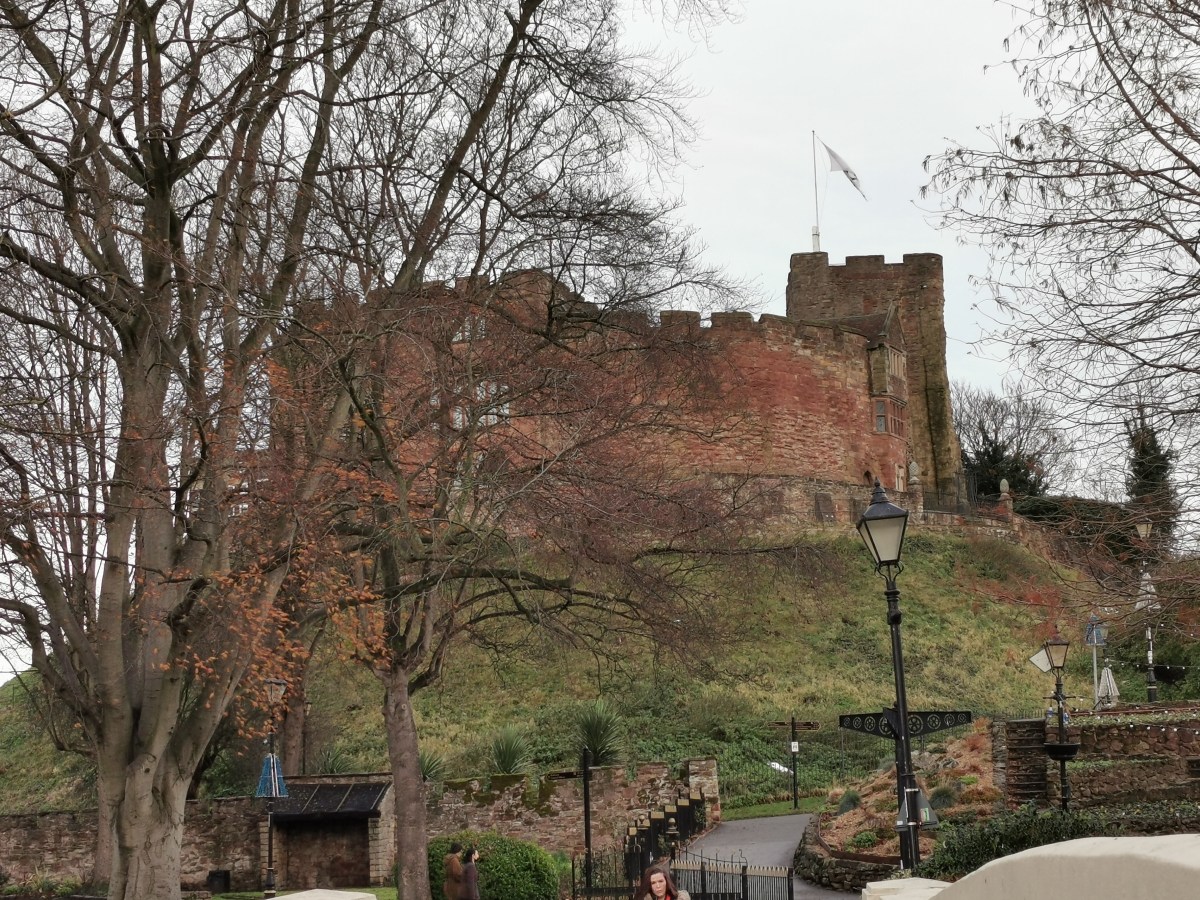
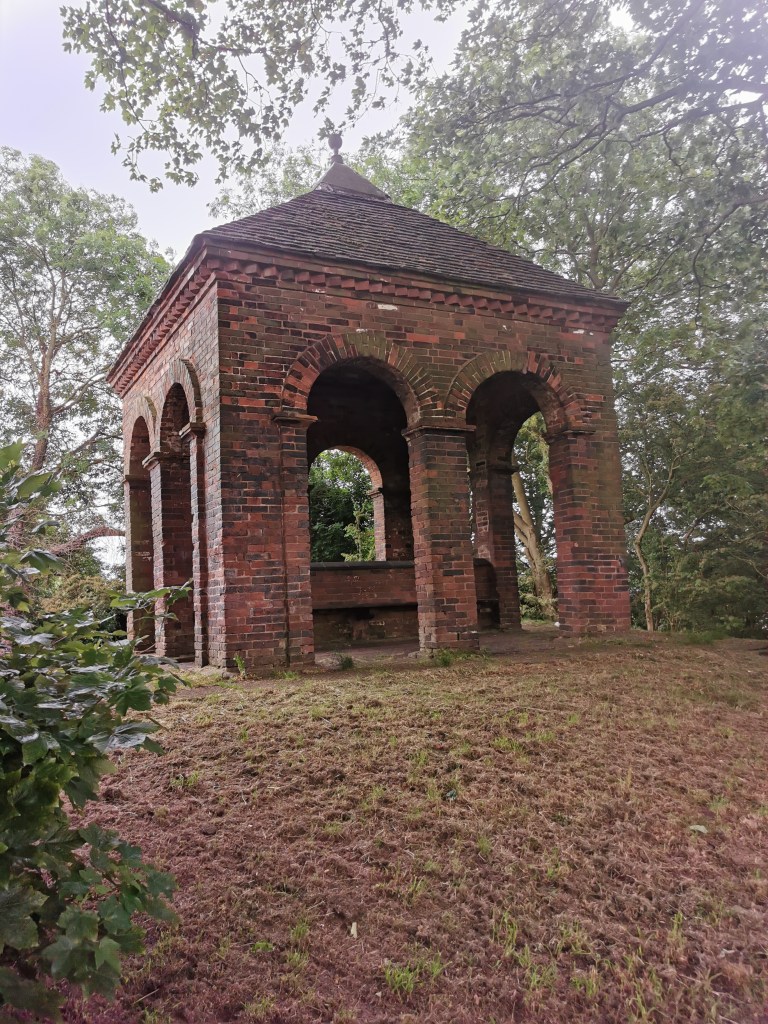
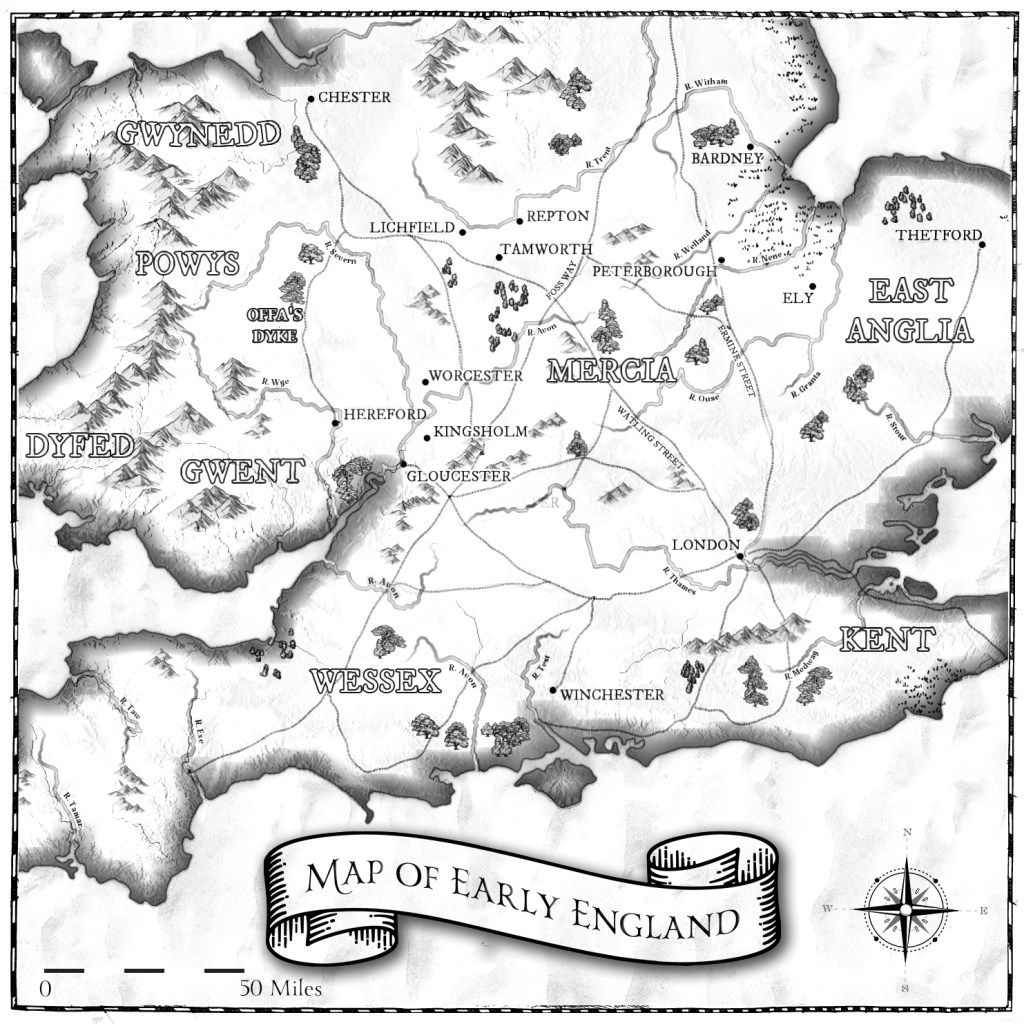
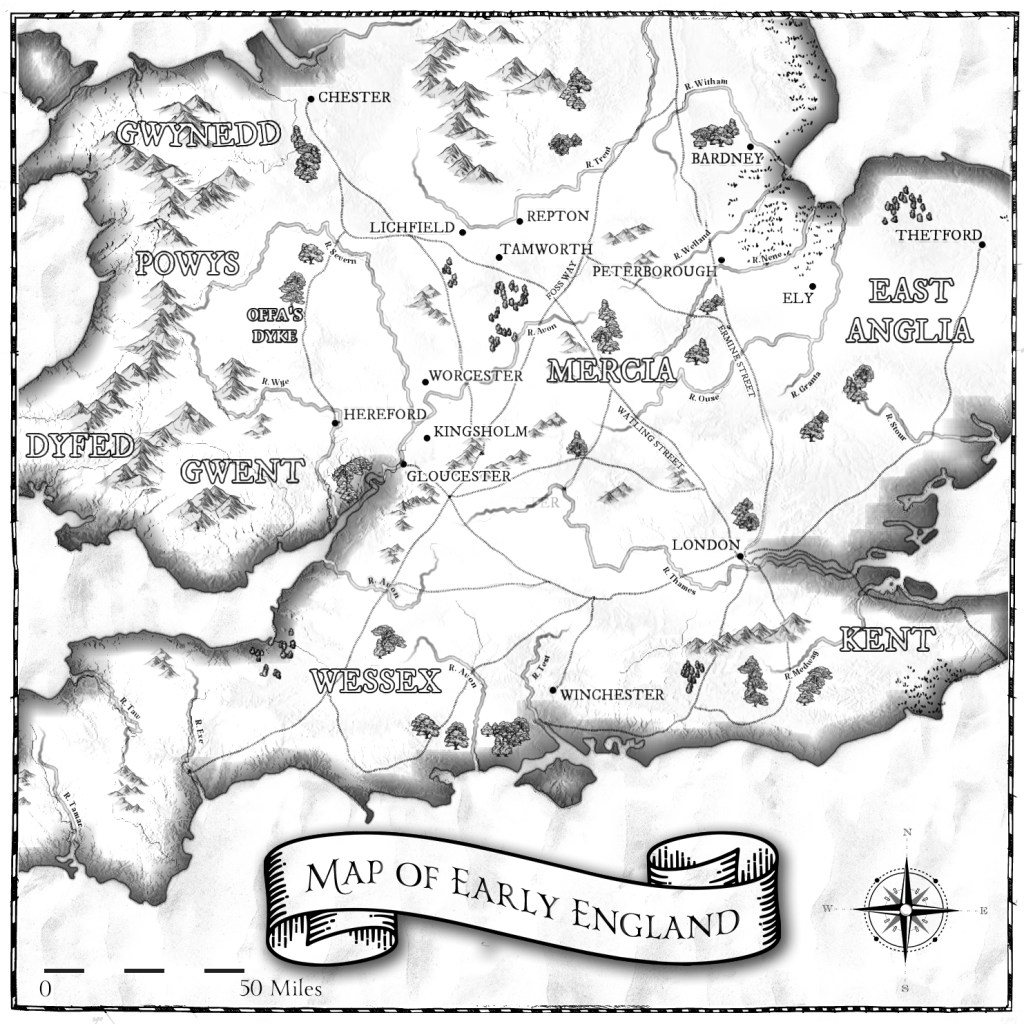
Like Lichfield and Repton, Tamworth has long been known to be a capital of the Saxon Mercian kingdom. Visitors today will find a more modern castle, which variously dates from the end of Saxon England up to the Victorian era, and one which is crammed with fascinating detail, from the herringbone wall beneath it to the beautiful Tudor windows of the great hall.
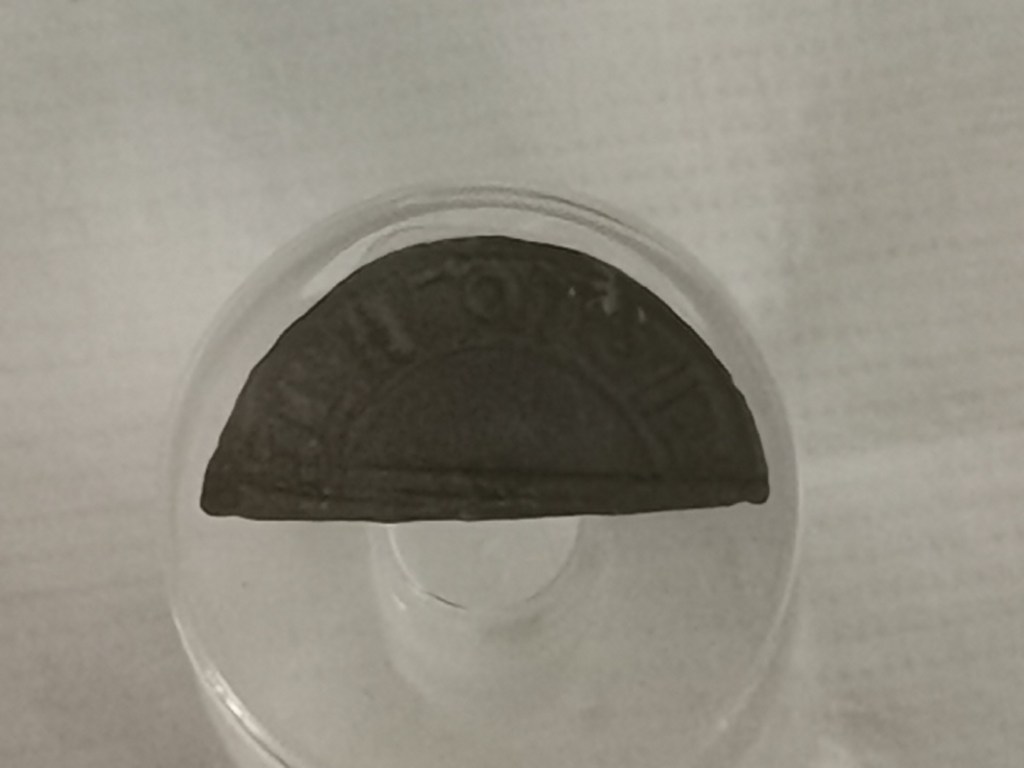
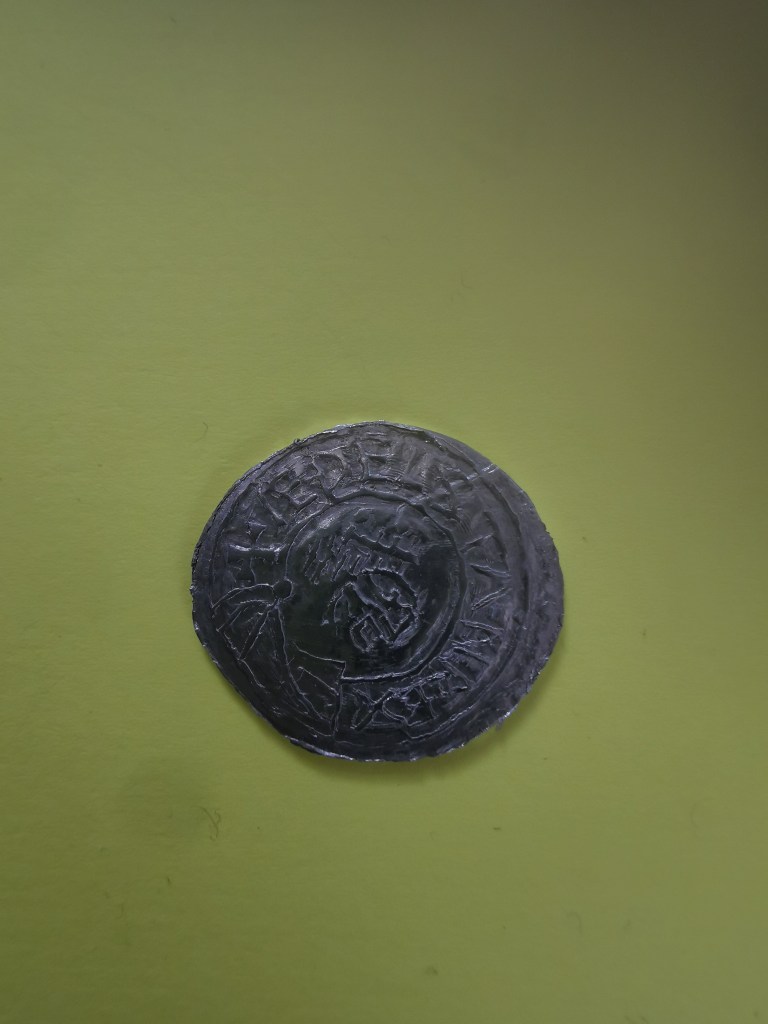
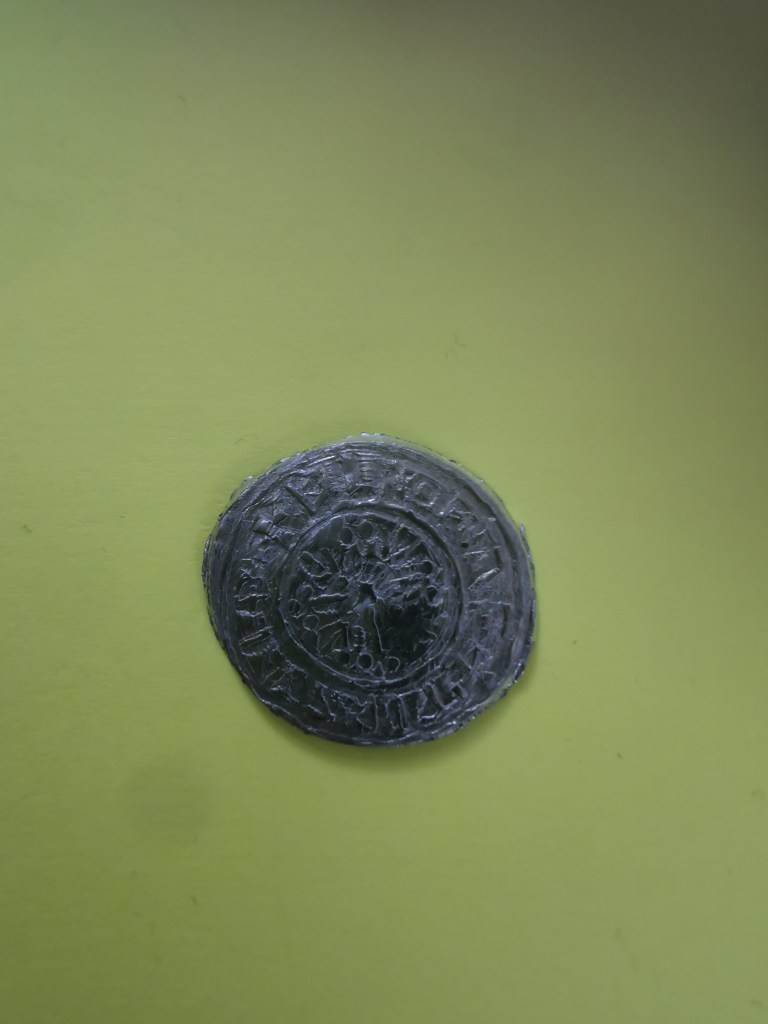
On a visit in 2021, I can also inform you that it currently had a third of the fabulous Staffordshire Hoard on display and an excellent museum filled with all things Saxon. (I believe it still holds some of the Staffordshire Hoard). Castles, if they were built in the late Saxon period, and some of them were, would have been constructed from wood. It was only later that they came to be built or rebuilt in stone, as we recognise them today.
Today’s castle wouldn’t have existed in the 820s and 830s. Indeed, it’s proven to be very difficult for archaeologists to determine where the original settlement of Tamworth lay, no doubt, because much of it has been overbuilt, just as in most places where habitation has been almost continuous. A fire in 1345 might well have destroyed any remaining wooden dwellings, making the endeavour even more difficult.
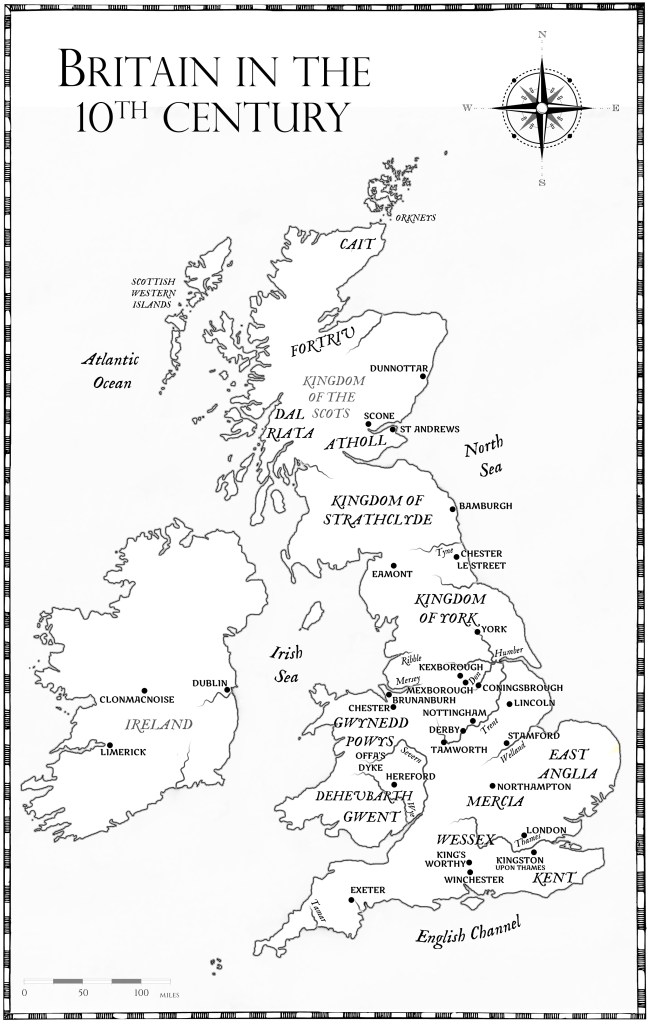
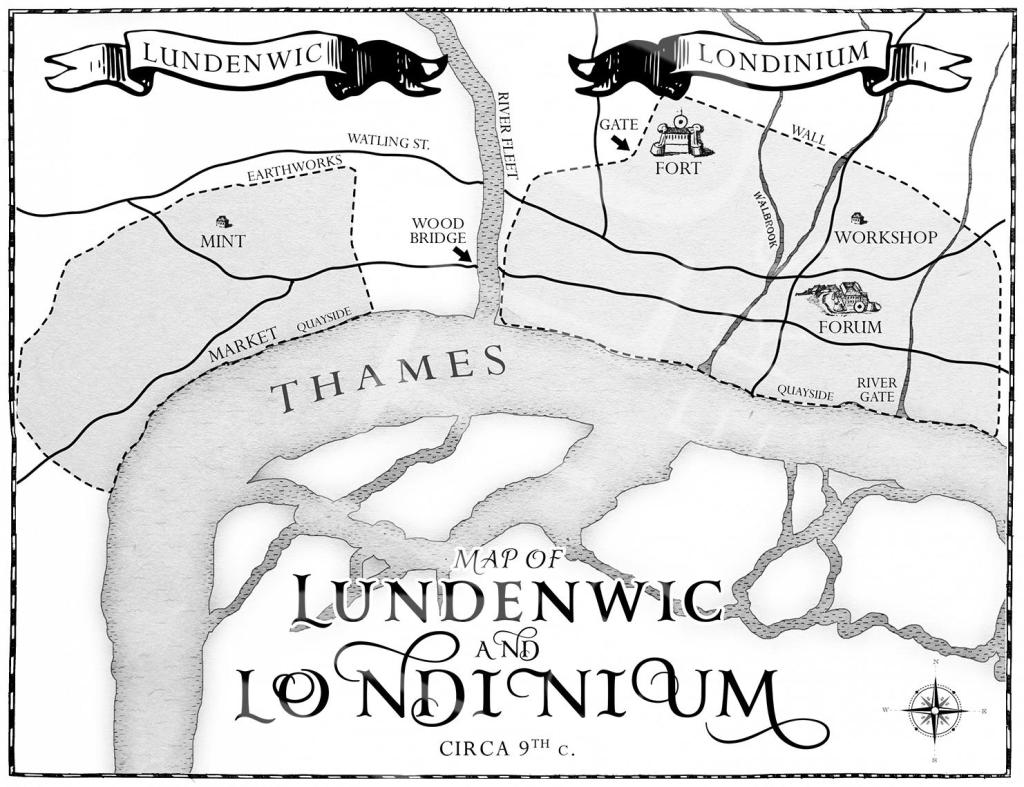
It has been possible to reconstruct Tamworth in the 900s, when it was designated a ‘burh,’ a defensive settlement in which the local population could seek shelter from the Viking raiders behind its walls. (I can’t find the image at the moment).
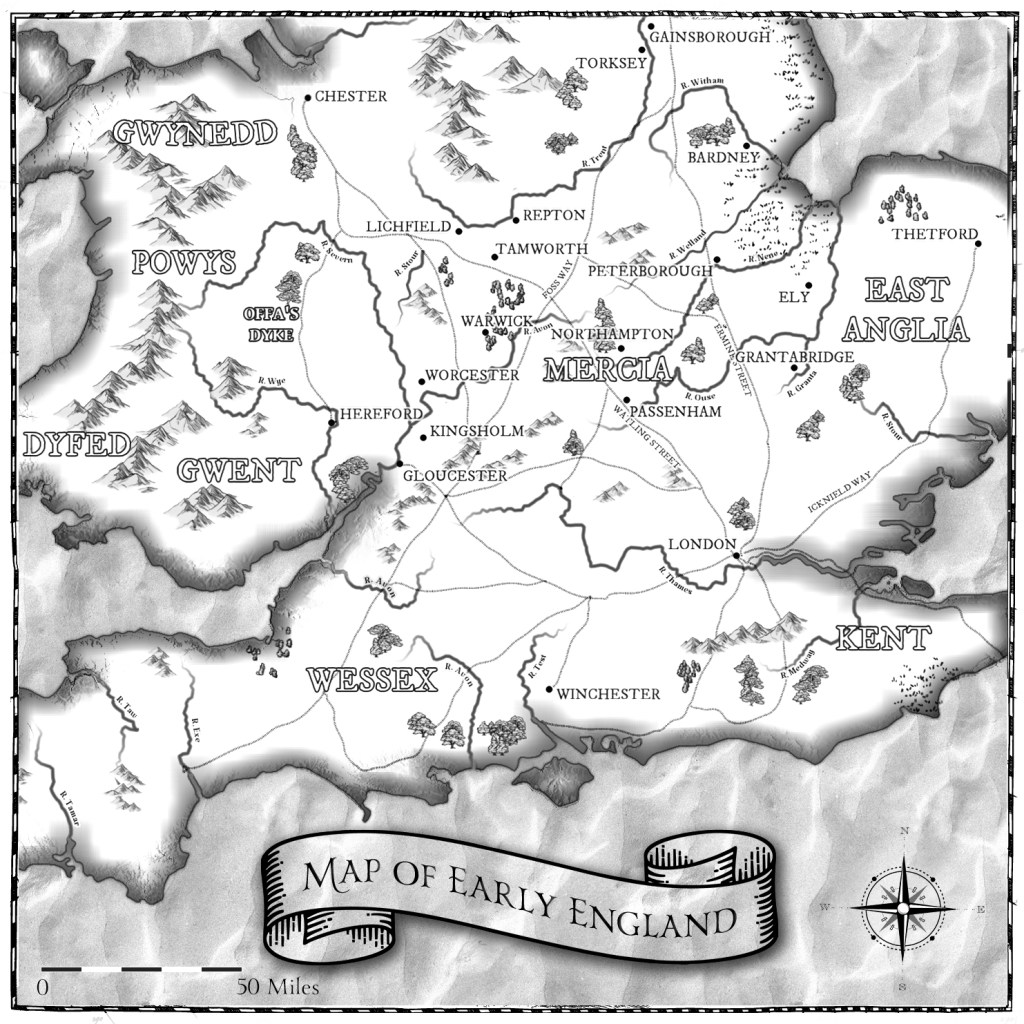
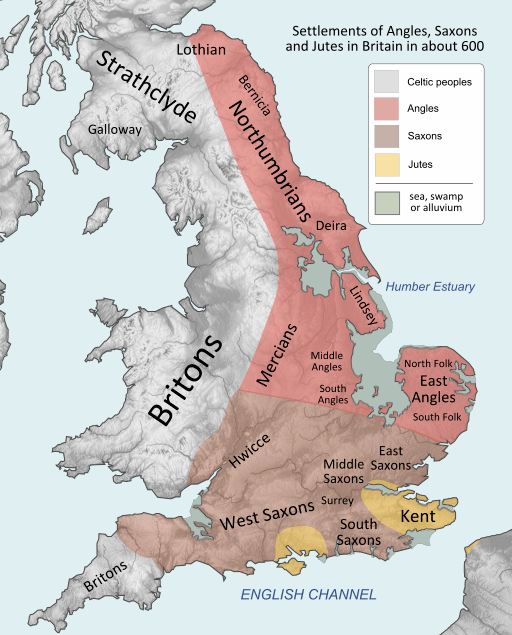
But it is possible to imagine how Saxon Tamworth might well have looked in the 800s, when the Eagle of Mercia Chronicles takes place. The rivers, The Tame and the Anker, run in front of the current castle, and there’s a slight rise, on which I used to spend many happy hours running up and down the steps, with flowers blooming in the flower beds. From there, it would have been possible to see a reasonable distance south. The river would have been put to good use, and the remains of a water mill have been found and dated to the later Saxon period. Houses would have been built from wood, wattle and daub with thatched roofs, and there would have been workshops as well as residential dwellings. At the centre of the settlement would have been a lord’s hall. While this hasn’t been found in Tamworth, it could have measured upwards of 24 metres long by 6 metres wide. It’s believed it was also surrounded by a defensive ditch. Somewhat sheltered, as the road to Lichfield is uphill, it would have been a pleasant, and I assure you, on the right day, very warm, location for Mercian kings to have lived within. It was close to Watling Street too, allowing easy access to the rest of Mercia.