Eboracum/Eoforwic/Jorvik
When I first wrote Kings of Conflict, I had very little idea what Jorvik at the time (the 930s/940s) might have looked like. I wrote an entire battle scene and then realised some of my assumptions were very, very wrong (I do this all the time. Don’t feel sorry for me. I should just do the research first instead of giving free rein to my imagination.) I got the fact the settlement was split in two by the River Ouse wrong (and who knew about the Foss). But, most tellingly, what I failed to understand was the true nature of York, from its Roman origins as Eboracum to the age of Jorvik, and most importantly by that I mean its Roman walls and what might, or might not have still been standing at this period.
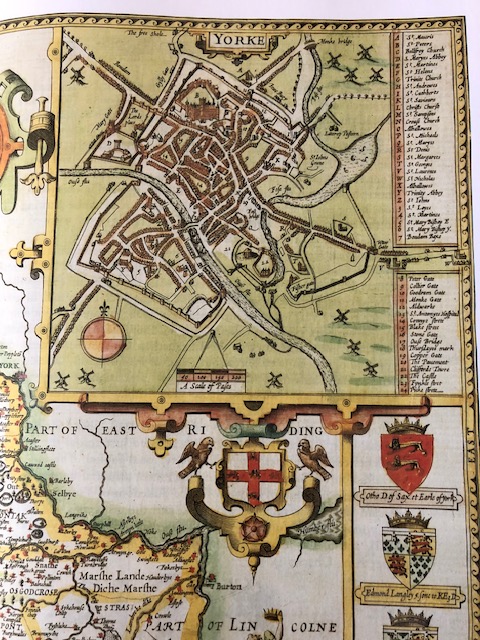
We don’t (yet) have time machines. We can’t visit York in the 940s, but if there is one thing York is famous for it’s the archaeology, and the Jorvik Viking Centre, which offers a recreation of what those streets on Coppergate might once have looked like, and also much else. And because Jorvik/York has benefitted from so much archaeological work, there are also a series of maps showing York at various times in its lifetime, alas out of print at this time, but which can be accessed via a good library (my thanks to the Great Northern Library at the Hancock museum in Newcastle – if you want to see it then let them know so they can have it ready for you, and make note of their opening hours) or the amalgamation of this work available in An Historical Map of York, available from all good book sellers. And if not, then my favourite ‘go-to’ for recreating this time period, the antiquarian maps by John Speed (which are also much prettier) can also offer some information.

Roman York
The British Historic Towns Atlas Volume V, York ed. Peter Addyman provides the following information about Eboracum-Roman York.


It might have been occupied under Vettius Bolanus (69-71) but was truly founded under Emperor Vespasian (69-79). However, the ridge of the River Ouse was a routeway from the Neolithic onwards. This was in the territory of the Brigantes although the East Riding of Yorkshire was that of the Parisi. It is possible that Eboracum means ‘the place of the yew trees.’
The stone used in constructing the fortress was Magnesian Limestone from Tadcaster and Millstone Grit from Bramham Park (I love that they know this). To begin with the fortress had a ditch, rampart and timber structures and four gates, with the original towers up to 15 metres high. And here, there is the suggestion that to begin with, crossing the River Ouse (to get to the civilian settlement) was via ferry. The bridge can only be confirmed from the second century onwards. The Foss River was also tidal at this time and the banks sloped sharply. The rampart was widened from 20feet to about 42 feet during a second phase of occupation.


The end of Roman York is impossible to pinpoint. Did it cease to exist? Certainly, the last documentary reference was in 314 when York’s bishop, Eborus, attended the Council of Arles, but as with so many of these Roman settlements in Britannia, what happened afterwards is more difficult to determine and we must turn to archaeology and not written records.
I must admit, all of this information about Roman York makes me somewhat desperate to write a book about it:) (Don’t all groan).
Anglian York – Eoforwic
The creators of this series of maps make the point that this is the most speculative of the series. Put simply, they really don’t know what was happening.
What can be said is that the walls were renovated on the north west side of the fortress with a dry stone wall and cobbled sentry walk while the eastern ramparts were topped with a timble palisade wider than the Roman wall (if I’ve understood that correctly).
Eoforwic first enters the historical record as the place of baptism for Edwin in 627, the king of Northumbria (Deira and Bernicia combined).
‘…the king was baptised at Easter with all his chief men; that Easter was on 12 April. This was done in York, where earlier he had ordered a church to be built of wood.’ ASC E 626 p.25
The archbishopric began from 735, but Eoforwic was not densely settled at this period, although it does seem to have had many, many churches. This includes the Minster, St Michael-Le-Belfrey, Holy Trinity, St Peter the Little, St Martin, St Michael, and many more, all probably founded by 850.
Viking York – Jorvik
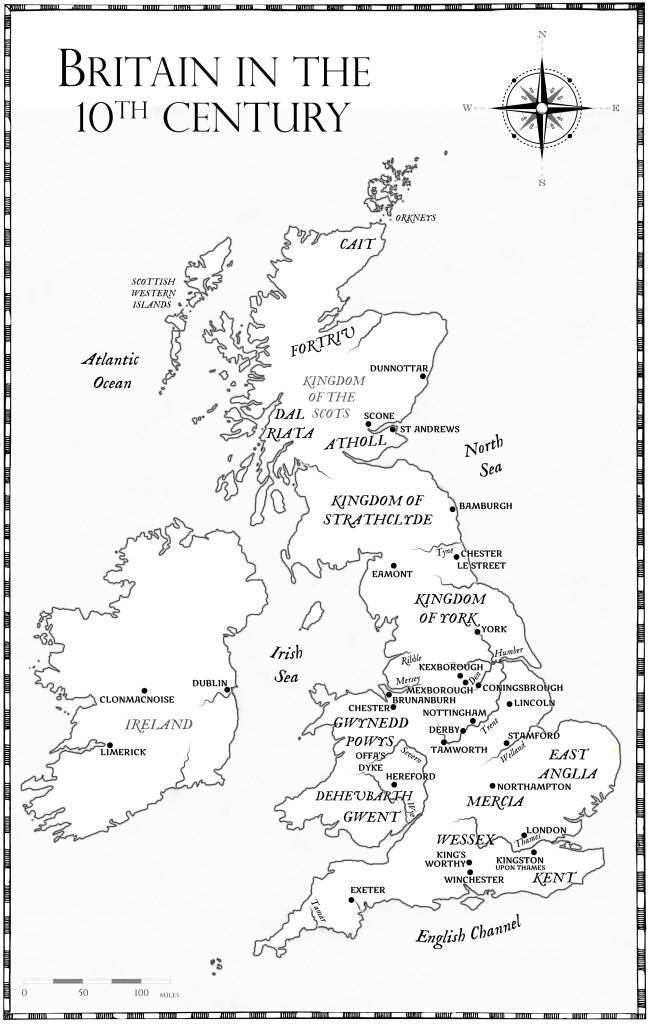
It’s record that the first attack Viking attack on York occured on 1st November 866. The Northumbrians counter-attacked in 867 but this left York under Viking control.
‘Here the raiding-army went from East Anglia over the mouth of the Humber to York city in Northumbria;’ ASC A 867 corrected to 866 p.68 (from my preferred edition edited by Michael Swanton).
And here is where my notes become a little muddled between time periods. The British Historic Towns Atlas Volume V informs that the River Ouse at the time would have been tidal, and much wider than it is now and also with much steeper banks .
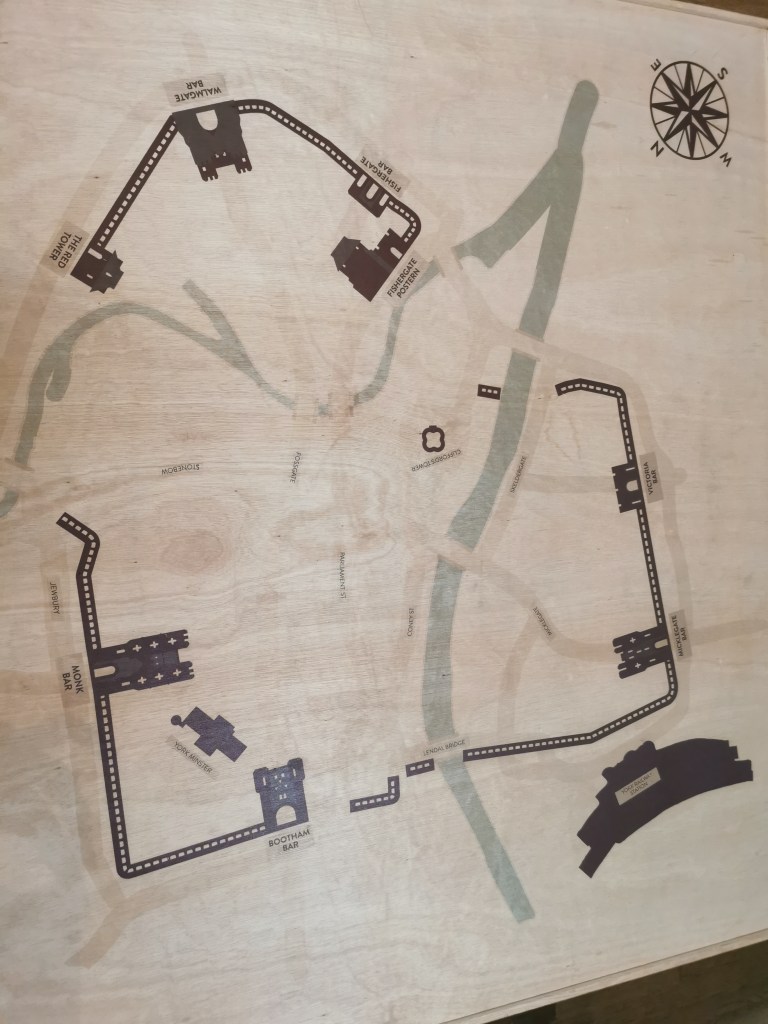
The late-eighth-century scholar Alcuin describes York as having high walls and lofty towers (he spent time in York). Asser (Alfred’s late-tenth-century biographer – although I’m curious as to how he’d know as I’m sure he was from one of the Welsh kingdoms and York was not under Alfred’s control) suggests that York’s walls were insecure and there is a suggestion that the Vikings restored the walls. Considering what we know about Asser and his ability to be less than honest, we might suspect this statement. Certainly, the remains of the walls were visible but whether they were defensible is unknown.
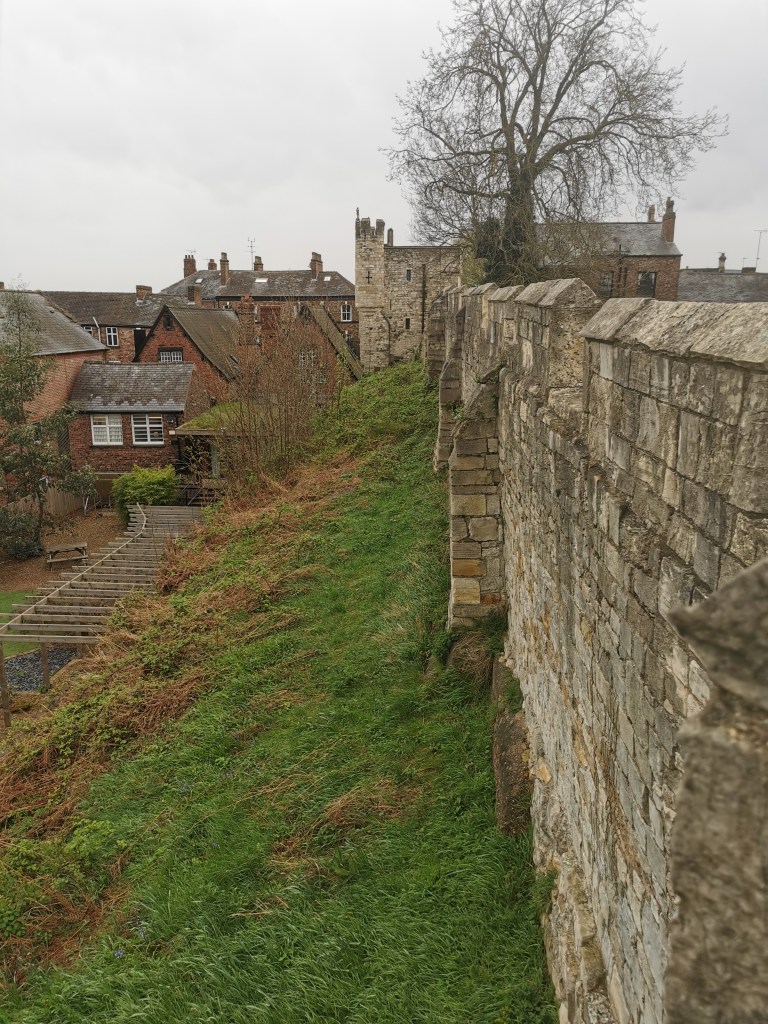
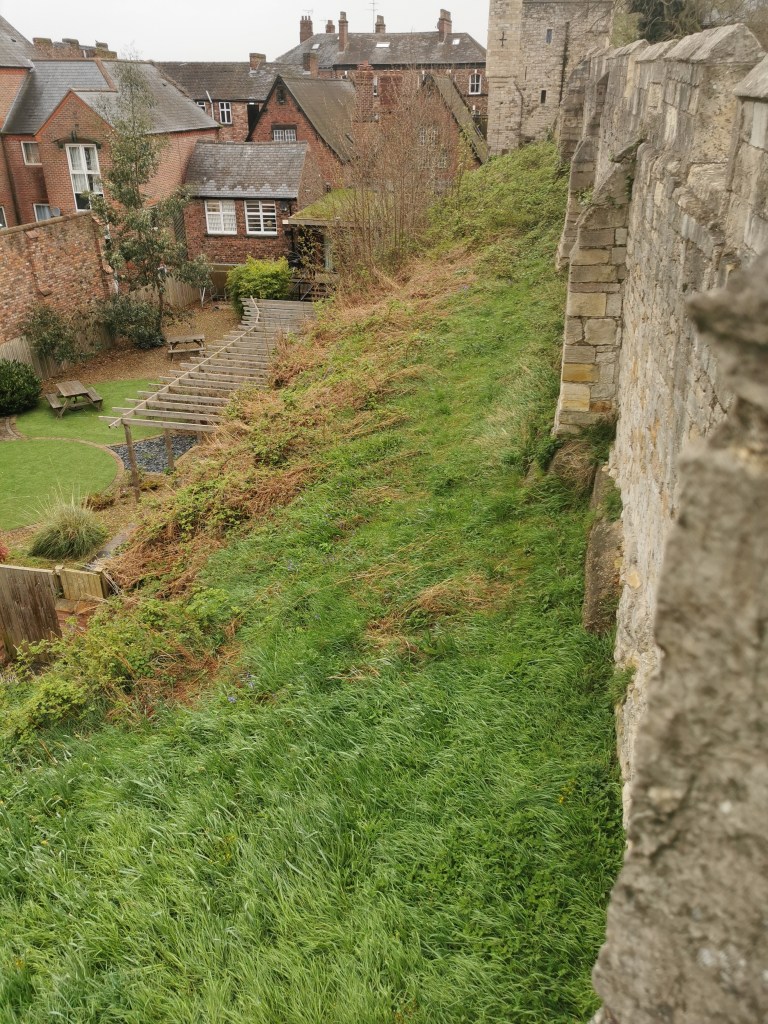
The walls survive to this day. To paraphrase from the Atlas, from the western corner of the Roman fortress to fifty metres along its south-west front, parallel to the river, the Roman wall is still visible above ground. Beyond this point, its six projecting interval towers and the Roman south/west gateway leading to the bridge over the Ouse have either been demolished to foundation level or been covered by organic-rich debris of post-Conquest date. The fortress’s south corner tower at Freasgate survives to fifteen foot. It is suggested that the south-west section of the civilian settlement might not have been included in the walled defences.
On the northern banks of the River Ouse, there were plots about 5.5m wide occupied by one or more structures (Coppergate/Ousegate/Pavement) with backyards running downslope towards the River Foss. Hungate also had similar plots. There might have been crossings over the rivers below St Mary Castlegate and Hungate. These rectangular structures of post and wattle had entrances front and back, with centrally arranged hearths and roofs made of turf, reeds or straw. Most settlement was below Coppergate, Ousegate, Pavement, Hungate and Walmgate areas.
Recreating Jorvik?
But what does all this mean when trying to recreate the time period? (Some will know that I’ve already ‘visited’ York earlier in the Brunanburh series, and without all this angst). It is frustrating that some aspects are so clearly defined and others aren’t. Where were the people living – especially the high status people? Where were the kings living? In King’s Square/Kuningesgard? And what’s this about the civilian defences never being completed to the south?
My overwhelming impression is that the remains of the actual Roman encampment (to the north of the Ouse) were in better condition than those to the south of the Ouse surrounding the civilian settlement (there are ‘proper’ terms for this – I’m not using them). But, these remains of the Roman wall at the fort seem to have largely been surrounding the religious centre under the control of the Archbishop of York, Wulfstan I. Were they any use to those in control of Jorvik? And what about the rivers? How navigable were they? Could they be easily blocked? How tidal is tidal? Did it raise and lower the water level by metres or centimetres?
Was there even a bridge over the River Ouse or did they need to use a boat to get across? Perhaps there was only one bridge over the Ouse, and only one over the River Foss.
Having this information to hand and making sense of it are two very different things. How would someone have gone about attacking York? Would they have taken ships, come on foot or tried to steal their way inside through the never completed walls? Who would have protected it? What would our erstwhile holy man, Archbishop Wulfstan have done? If the walls were standing, how many warriors would have needed to protect it?
You’ll have to read Conflict of Kings to see just what I did, and you can from 6th August 2024:)
books2read.com/KingsOfConflict10th