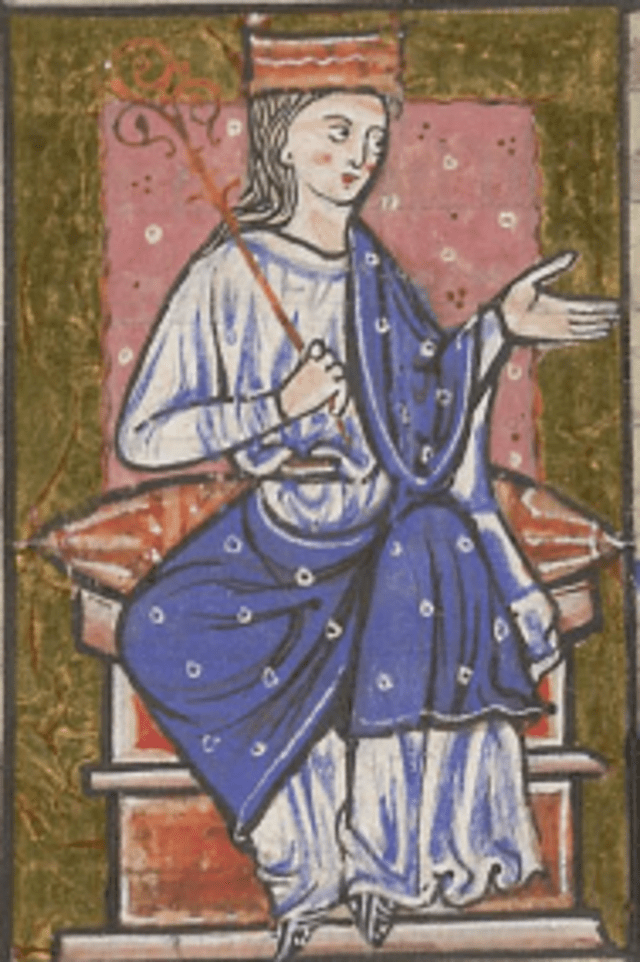
Athelstan is one of the main characters in my new book, King of Kings, a multiple point of view story, recounting affairs in Britain from 925-934.
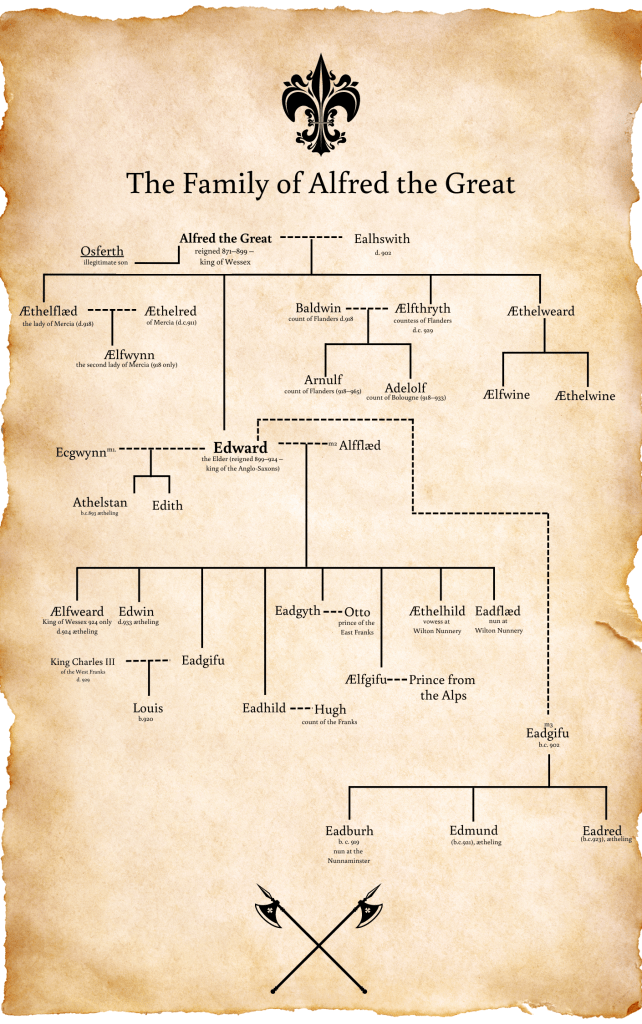
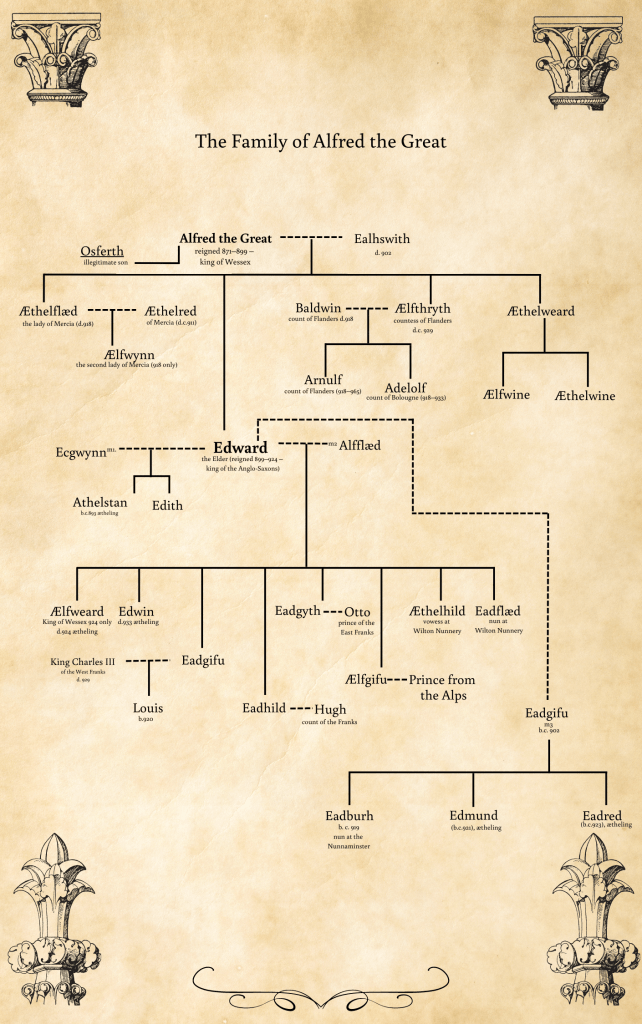
Based on a historical person, my portrayal of him, is of course, fictitious, but there are many details known about him. However, we don’t know for sure who his mother was, it’s believed she might have been called Ecgwynn, and we don’t know, for certain, the name of his sister, but it’s believed she might have been named Edith. What is known is that his father was Edward, the son of King Alfred, and known to us today as Edward the Elder. Athelstan is also rare in that he is one of only two Saxon kings for who a contemporary image is available. (The other is Edgar, who would have been his step-nephew)
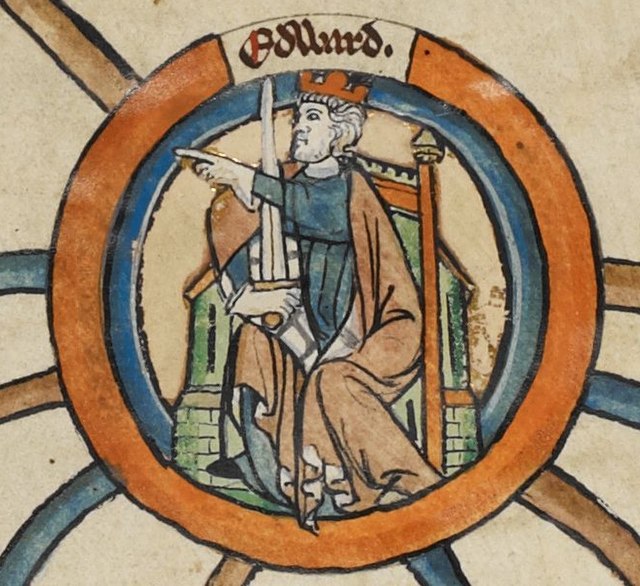

Edward the Elder – MS Royal 14 B VI.jpg
Miniature d’Édouard l’Ancien dans une généalogie royale du XIVe siècle. WikiCommons
It must be supposed that Athelstan was born sometime in the late 890s. And according to a later source, that written by William of Malmesbury in the 1100s (so over two hundred years later), Athelstan was raised at the court of his aunt, Æthelflæd of Mercia. David Dumville has questioned the truth of this, but to many, this has simply become accepted as fact.
‘he [Alfred] arranged for the boy’s education at the court of his daughter, Æthelflæd and Æthelred his son in law, where he was brought up with great care by his aunt and the eminent ealdorman for the throne that seemed to await him.’[i]
[i] Mynors, R.A.B. ed and trans, completed by Thomson, R.M. and Winterbottom, M. Gesta Regvm Anglorvm, The History of the English Kings, William of Malmesbury, (Clarendon Press, 1998), p.211 Book II.133
Æthelflæd image
Æthelflæd as depicted in the cartulary of Abingdon Abbey (British Library Cotton MS Claudius B VI, f.14).
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Æthelflæd_as_depicted_in_the_cartulary_of_Abingdon_Abbey.png
AnonymousUnknown author, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Why then might this have happened? Edward became king on the death of his father, Alfred, and either remarried at that time, or just before. Edward’s second wife (if indeed, he was actually married to Athelstan’s mother, which again, some doubt), Lady Ælfflæd is believed to have been the daughter of an ealdorman and produced a hefty number of children for Edward. Perhaps then, Athelstan and his unnamed sister, were an unwelcome reminder of the king’s first wife, or perhaps, as has been suggested, Alfred intended for Athelstan to succeed in Mercia after the death of Æthelflæd, and her husband, Æthelred, for that union produced one child, a daughter named Ælfwynn.
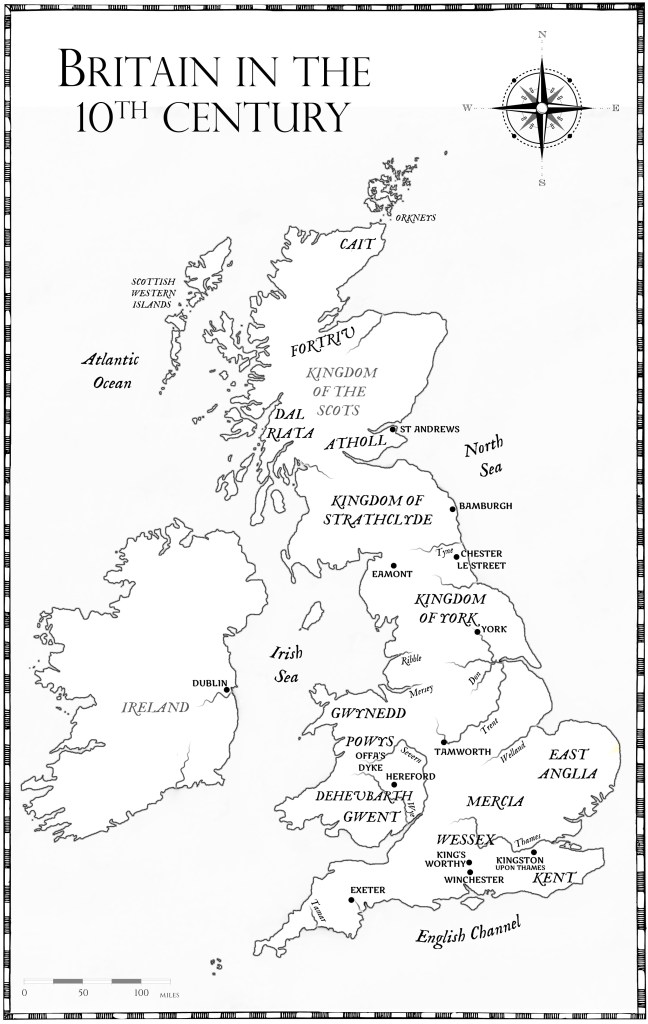
There is an acknowledged dearth of information surrounding King Edward the Elder’s rule of Wessex. He’s acknowledged as the king of the Anglo-Saxons. His father had been the king of Wessex. Historians normally use the surviving charters to unpick the political machinations of the Saxon kings, but for Edward, there’s a twenty year gap between the beginning and end of his reign, where almost no known genuine charters have survived. What isn’t known for sure, is how much control, if any, he had in Mercia. Was Mercia subservient to Wessex or was it ruled independently? It’s impossible to tell. And this makes it difficult to determine what Athelstan might have been doing, and also what his father’s intentions were towards him.
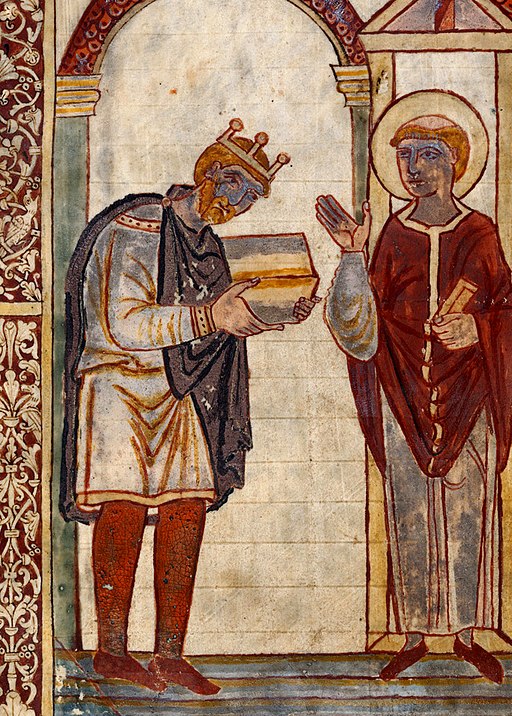

What is known is that following the death of King Edward in 924, Athelstan was acknowledged as the king of Mercia; his stepbrother, Ælfweard was proclaimed king in Wessex. As with all events at this time, it shouldn’t be assumed that just because this is what happened, this is what was always intended.
‘Here King Edward died at Farndon in Mercia; and very soon, 16 days after, his son Ælfweard died at Oxford; and their bodies lie at Winchester. And Athelstan was chosen as king by the Mercians and consecrated at Kingston.’[i]
[i] Swanton, M. trans and edit The Anglo-Saxon Chronicles, (Orion Publishing Group, 2000), D text p.105
But, if Athelstan was raised in Mercia, it’s highly likely he was a warrior from a young age, helping the Mercians defeat the Viking raiders who still had control of the Danish Five Boroughs of Lincoln, Nottingham, Derby, Nottingham and Leicester.
And the events of 924 are where King of Kings begins, and so I will leave him there. By now, he would have been perhaps thirty years old, give or take a few years. What sort of man was he? What sort of king might he be? Do please read King of Kings to find out. And, if this intrigues you, then do please have a look at Sarah Foot’s wonderful monograph on him, Athelstan, from Yale Publishing.
Preorder King of Kings now
(released 20th February 2023)
Meet Hywel, king of the West Welsh
Meet Constantin, king of the Scots
Meet Lady Eadgifu, queen of the Anglo-Saxons