I’m delighted to welcome Katerina Dunne and her new book, Return to the Eyrie from the Medieval Hungary series to the blog with The Siege of Szabács (1476).
The Siege of Szabács (1476)
During his long reign (1458-1490), King Mátyás of Hungary faced the Ottoman army many times. Although the King kept a rather defensive stance against Sultan Mehmed’s advances towards Central Europe, he did his best to ensure the border raids perpetrated by the Ottomans remained localised. Mátyás focused on expanding his kingdom to the west and north; but when circumstances demanded it, he fought the Ottomans successfully.
Several chapters of Return to the Eyrie are dedicated to the siege of Szabács (Jan-Feb 1476) It is where the young heroine, Margit, receives her baptism of fire as a soldier. Dressed in a man’s clothes, she puts her archery and fighting skills to the test.
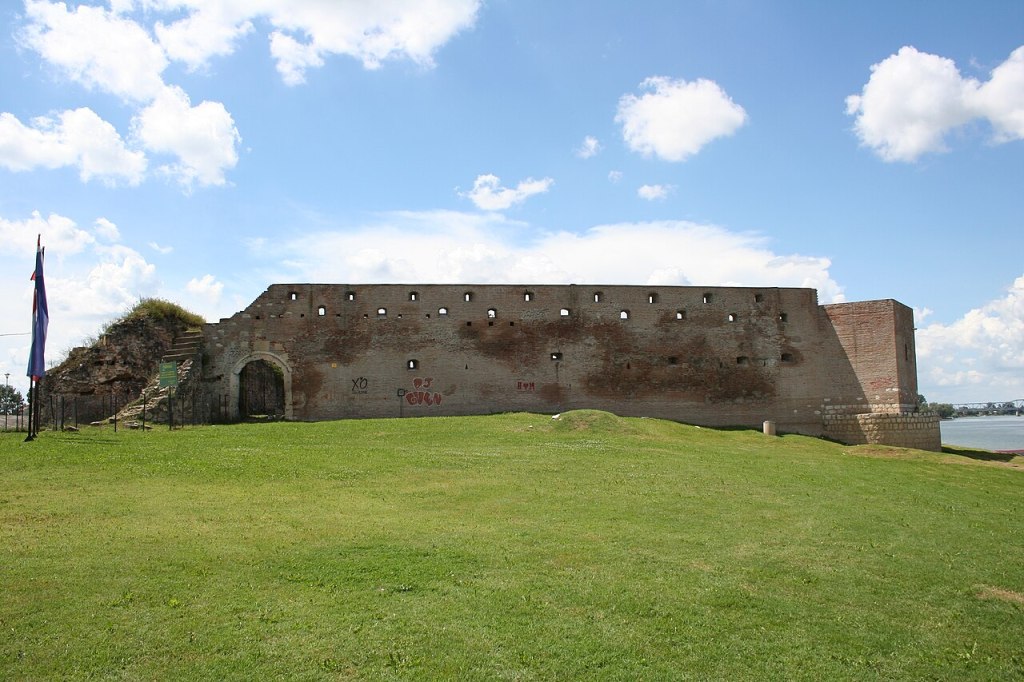
The fortress of Szabács (Šabac in Serbian) was a stronghold on the southern bank of the river Sava. It was built in 1470 by the Ottomans, who had occupied the area since 1459 and used the fortress as a base to launch raids into the territories of the Kingdom of Hungary (mainly Croatia, Slavonia and the Hungarian-occupied area around Belgrade)
According to sources of the time, the fortress was constructed of wood and rammed earth and was surrounded by marshes as well as man-made ditches. This whole arrangement was quite effective against bombardment.
After fighting against his Christian neighbours for many years, King Mátyás wished to pacify public opinion in Hungary and abroad and present himself as a “defender of the faith”. During 1475, he had already established a huge army of Hungarian, Transylvanian, Wallachian and mercenary forces, including artillery and siege equipment as well as river galleys and gunboats.
It is not exactly certain whether his plan at the time was to go to the aid of the Moldavian and Wallachian princes, whose territories were threatened by an Ottoman invasion, or capture the main Ottoman fortresses in Serbia in order to stop the enemy attacks against his own kingdom. In any case, he ended up besieging Szabács in January and February 1476 from land and river with a force that severely outnumbered the Ottoman defenders and discouraged any relief army to approach the fortress.
The earthen walls of Szabács withstood the long-range bombardment during the first part of the siege while the Ottoman arrows and firearms prevented any assault from the land. But when the waters in the ditches rose in the first days of February, the war galleys were able to approach from the river and intensify the damage to the walls. This, together with bombardment and assaults from the land, broke the Ottoman resistance, and the defenders surrendered on 15 February 1476.
In his chronicle, Antonio Bonfini wrote that Mátyás took the fortress by employing a ruse: he feigned retreat while a part of his army hid in a neaby forest. When the Ottomans thought the danger had passed and relaxed their guard, the hidden soldiers climbed the walls and took Szabács. Although this story has great dramatic effect (which I partly use in my novel), it was probably only a myth.
Another primary source of the time, the anonymous poem Szabács Viadala (The Fight for Szabács), presents a more plausible version of how the fortress was taken. In the poem, an Ottoman soldier, who still remembered his Hungarian origin, fled and revealed the weak points of the fortifications to Mátyás. The bombardment then concentrated on these areas until the fotress fell.
Whatever the real reason for the capture of Szabács was, historian Tamás Pálosfalvi suggests that its significance rests on the King’s original intentions at the time. If Mátyás had intended to assist Moldavia and Wallachia but was forced to change his plans due to the adverse weather or the failure of the Ottomans to attack Wallachia at the time, then the victory at Szabács can be considered a success. If, however, Szabács was his main aim, then the whole operation only served to convince public opinion in Hungary and abroad of the King’s commitment to defending Christendom against the Ottoman danger.
Works Consulted:
Antonio Bonfini: A Magyar Történelem Tizedei (Rerum Hungaricarum Decades), Hungarian trans. P. Kulcsár (Budapest, 1995)
Szabács Viadala (The Fight for Szabács)—a poem commemorating the siege and capture of Szabács (author anonymous; date unknown but possibly around the time of the siege in 1476)
https://magyar-irodalom.elte.hu/gepesk/kkor/049.htm
Pálosfalvi, T., From Nicopolis to Mohács: A History of Ottoman-Hungarian Warfare, 1389–1526 (Leiden, 2018)
Sources
The remains of the Šabac / Szabács fortress photo by Ванилица from Wikipedia : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/%C5%A0abac_Fortress#/media/File:%C5%A0abac,_%C5%A0aba%C4%8Dka_tvr%C4%91ava_013.jpg
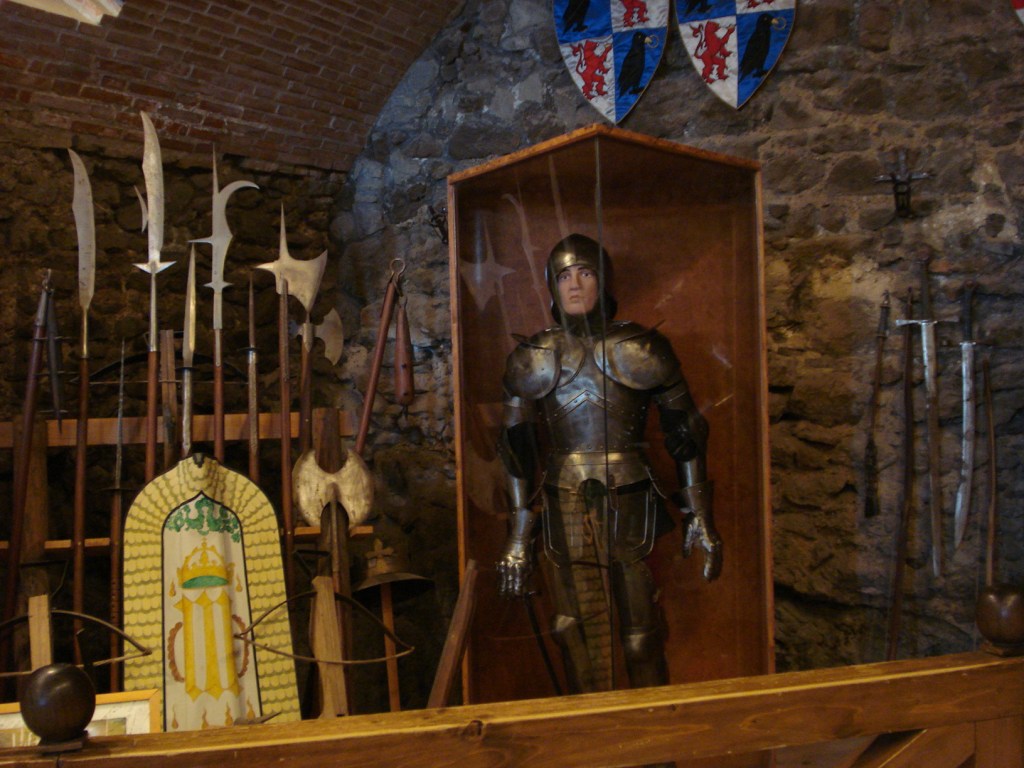
Armour and weapons of King Mátyás’ soldiers at the Visegrád citadel museum (my photo)
Blurb
Honour, revenge, and the quest for justice.
Belgrade, Kingdom of Hungary, 1470:
Raised in exile, adolescent noblewoman Margit Szilágyi dreams of returning to her homeland of Transylvania to avenge her father’s murder and reclaim her stolen legacy. To achieve this, she must break the constraints of her gender and social status and secretly train in combat.
When the king offers her a chance at justice, she seizes it—even if it means disguising herself as a man to infiltrate the vultures’ nest that now occupies her ancestral ‘eyrie’.
Plagued by childhood trauma and torn between two passionate loves, Margit faces brutal battles, her murderous kin’s traps and inner demons on her quest for vengeance. Only by confronting the past can she reclaim her honour—if she can survive long enough to see it through.
Return to the Eyrie is an epic coming-of-age tale of a young woman’s unwavering pursuit of justice and destiny in 15th century Hungary.
Buy Link
Meet the Author
Katerina Dunne is the pen-name of Katerina Vavoulidou. Originally from Athens, Greece, Katerina has been living in Ireland since 1999. She has a degree in English Language and Literature from the University of Athens, an MA in Film Studies from University College Dublin and an MPhil in Medieval History from Trinity College Dublin.
Katerina is passionate about history, especially medieval history, and her main area of interest is 13th to 15th century Hungary. Although the main characters of her stories are fictional, Katerina uses real events and personalities as part of her narrative in order to bring to life the fascinating history of the medieval Kingdom of Hungary, a location and time period not so well-known to English-speaking readers.
Return to the Eyrie (published April 2024) is the second book in the Medieval Hungary series, a sequel to Lord of the Eyrie (published in February 2022).
Connect with the Author