The King’s Daughters is available with Kindle Unlimited, and is a novel of the many daughters of Edward the Elder who married into the ruling families in East and West Frankia, or who became holy women, or lived within a nunnery.


So, who were these daughters?
Edward the Elder was married three times, to an unknown woman- who was the mother of the future King Athelstan, to Lady Ælfflæd – who was the mother of the future, and short-lived King Ælfweard, and finally to Lady Eadgifu – who was the mother of the future kings Edmund and Eadred. But, while each woman was mother to a future kings, this story focuses on the daughters. And there were a lot of them, and their lives were either spent in making prestigious marriages, or as veiled women – whether professed religious, or merely lay women living in a nunnery or an isolated estate.
The story of The King’s Daughters is very much about the daughters of Edward and his second wife, and the marriages they made in Continental Europe, into the powerful families in East and West Frankia. And I’ve written a lengthy post about them which you can find here. But there were other daughters/sisters, and while their lives might be almost lost to us, it is interesting to discover what little is known of them.
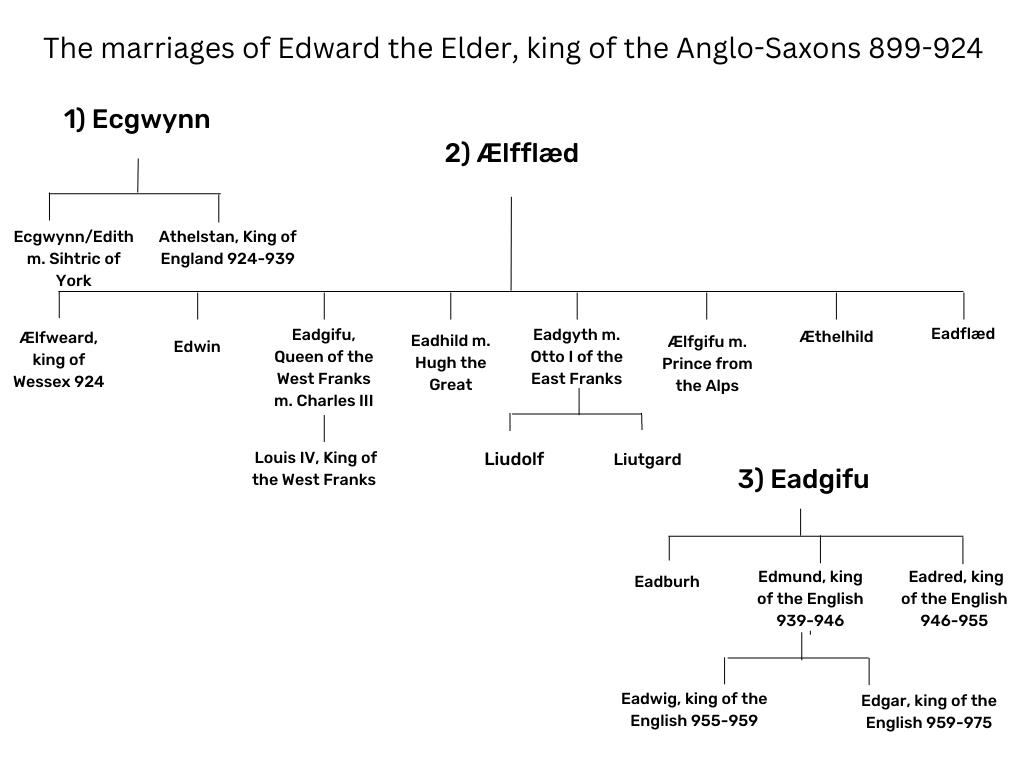
Edith/Eadgyth/Ecgwynn/unnamed daughter of Edward the Elder, and his unnamed first wife (Ecgwynn?) c.890s–937?
m. Sihtric, king of York in 925, repudiated by 927 when Sihtric died
Edith[i] is believed to be the biological sister of the future King Athelstan, and, therefore, the daughter of King Edward and his first wife, possibly named Ecgwynn. Edith is unnamed in the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, but her marriage is mentioned in both the D and the C texts.
The C text records that in 924, ‘Athelstan was chosen as king by the Mercians, and consecrated at Kingston, and he gave his sister.’[ii] And here the text, rather enigmatically, comes to a halt until 954.
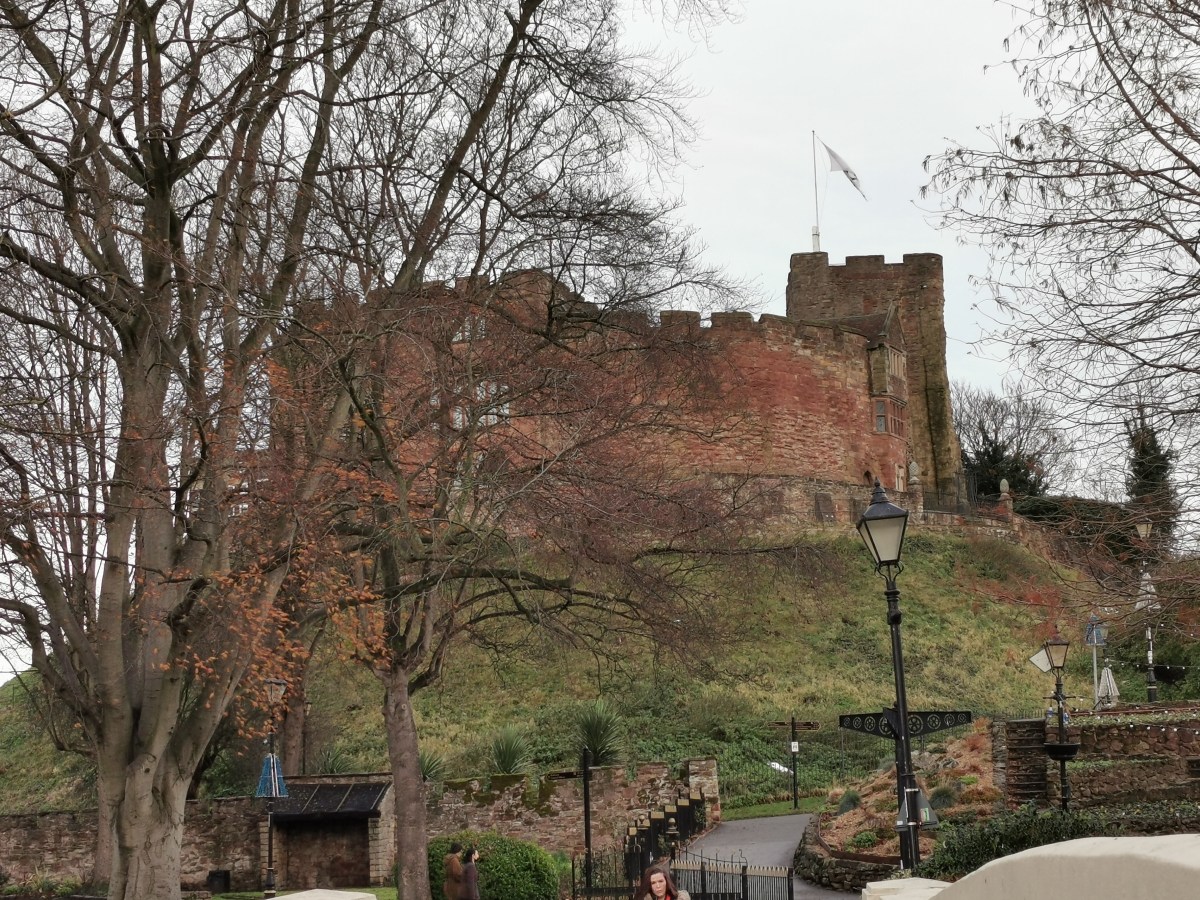
The D text, is rather more helpful, under 925 stating that, ‘Here Athelstan and Sihtric, king of Northumbria, assembled at Tamworth on 30th January, and Athelstan gave him his sister.’[iii]
This, therefore, refers to the union between Athelstan’s sister and Sihtric, a Norse king of Jorvik or York. The union is intriguing. It does seem to be the only occasion that a marriage union was enacted between the Viking raiders and the Wessex royal family.
There is the suggestion that Edith may have become a nun on her return to Mercia. She is associated with the nunnery at Polesworth by traditions recorded at Bury in the twelfth century. Following the death of her husband, she is said to have returned to Mercia and ‘founded a nunnery at Polesworth, near the Mercian royal centre at Tamworth. There she remained a virgin, practising fastings and vigils, offering prayers and alms to the end of her life, and dying on July 15.’[iv]
However, Thacker goes on to state that, ‘it must be admitted that it [the cult] was not a very successful one. Her feast day (15 July) occurs in only three relatively late (i.e. post-Conquest) calendars, and it is impossible to identify her in any of the surviving Anglo-Saxon litanies.’[v]
[i] Edith may be Anonymous (594) or Eadgyth (12) on PASE, in which case her death was c.937
[ii] Swanton, M. ed. and trans. The Anglo-Saxon Chronicles, (Orion Publishing Group, 2000), p.105
[iii] Ibid., p.105
[iv] Thacker, A. ‘Dynastic Monasteries and Family Cults’, in Edward the Elder, 899–924, ed. Higham & Hill (Routledge, 2001), p.257
[v] Thacker, A. ‘Dynastic Monasteries and Family Cults’, in Edward the Elder, 899–924, ed. Higham & Hill (Routledge, 2001), p.258
Æthelhild, daughter of Edward the Elder, and his second wife, Lady Ælfflæd
The birth order of Edward the Elder’s children is unknown. Therefore, we do not know why Æthelhild[i] became a lay sister at Wilton Abbey. Could it be because it was her choice, her father’s, or mother’s, or that of her half-brother, Athelstan?
Wilton Abbey was strongly associated with the Wessex royal family. Her sister Eadflæd became a nun, and the two sisters were joined, not only by their mother but also by their much younger half-sister, Eadburh. Nothing further is known of Æthelhild. She’s not mentioned in the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, or in any of the surviving charter evidence. We don’t know her date of birth, or her date of death.
William of Malmesbury’s Gesta Regum Anglorum tells us more.
He also had by the same wife six daughters; Eadflæd, Eadgifu, Æthelhild, Eadhild, Eadgyth, Ælfgifu. The first and third took a vow of virginity and spurned the pleasures of earthly marriage, Eadflæd took the veil and Æthelhild in lay attire; both lie at Wilton, buried next to their mother. Eadburh became a nun and lies at Winchester; Eadgifu was a famous beauty, and was given in marriage by her brother Æthelstan to Louis prince of Aquitaine.[i]
[i] Mynors, R.A.B. ed. and trans. completed by Thomson, R.M. and Winterbottom, M. Gesta Regvm Anglorvm, The History of the English Kings, William of Malmesbury, (Clarendon Press, 1998) p.199–201
Eadflæd, daughter of Edward the Elder, and his second wife, Lady Ælfflæd
Eadflæd[iii] became a nun at Wilton Abbey. And she is named in a charter issued by Athelstan (S438, surviving in one manuscript) granting land to St Mary’s, Wilton dated 937, the year of the battle of Brunanburh. Provided the dating is secure, and the charter is authentic, this points to Eadflæd still being alive at this date. The absence of her sister’s name, Æthelhild, may mean she had predeceased her sister. Note should be made here of the distinction between the two types of religious women. It is believed that there were lay sisters and also those who wore the veil. Both could have been attached to a nunnery, although, aside from the Nunnaminster, no religious establishment is specifically termed as a monastery for women.
Eadburh, c.919–952 daughter of Edward the Elder and his third wife, Eadgifu
William of Malmesbury in his Gesta Pontificum Anglorum tells the story of Edward the Elder’s youngest daughter, Eadburh,[v] being consigned to the Nunnaminster in infancy as she showed such signs of devotion:[vi]
There had been a convent on this spot before, in which Eadburg [Eadburh], daughter of king Edward the Elder, had lived and died, but by then it was almost in ruins. When she was barely three, Eadburg had given a remarkable proof of her future holiness. Her father had wanted to find out whether his little girl would turn towards God or the world. He set out in the dining room the adornments of the different ways of life, on this side a chalice and the Gospels, on the other bangles and necklaces. The little girl was brought in by the nurse and sat on her father’s knees. He told her to choose which she wanted. With a fierce look she spat out the things of the world, and immediately crawling on hands and knees towards the Gospels and chalice adored them in girlish innocence … Her father honoured his offspring with more restrained kisses and said, ‘Go where heaven calls you, follow the bridegroom you have chosen and a blessing be upon your going.’ … Countless miracles during her life and after her death bear witness to the devotion of her heart and the integrity of her body.[vii]
William later adds that ‘Some of the bones of Eadburg the happy are buried’,[viii] at Pershore.
Aside from the later William of Malmesbury, Eadburh is the recipient to land in one charter, that of S446, dated to 939 and surviving in one manuscript. ‘King Athelstan to Eadburh, his sister; grant of 17 hides (mansae) at Droxford, Hants.’[ix] Perhaps, Athelstan was ensuring his sister’s future with this charter. Maybe he knew he was dying. Perhaps this was a means of guaranteeing the survival of the religious establishment in which she lived.
[i] I can find no reference to Æthelhild on PASE
[ii] Mynors, R.A.B. ed. and trans. completed by Thomson, R.M. and Winterbottom, M. Gesta Regvm Anglorvm, The History of the English Kings, William of Malmesbury, (Clarendon Press, 1998), pp.199–201
[iii] PASE Eadflæd (4)
[iv] Mynors, R.A.B. ed. and trans. completed by Thomson, R.M. and Winterbottom, M. Gesta Regvm Anglorvm, The History of the English Kings, William of Malmesbury, (Clarendon Press, 1998), pp.199–201
[v] Believed to be Eadburgh (8) on PASE
[vi] Foot, S. Athelstan (Yale University Press, 2011), p.45 Priest, D. trans. Gesta Pontificum Anglorum, The Deeds of the Bishops of England, (The Boydell Press, 2002)
[vii] Priest, D. trans. Gesta Pontificum Anglorum, The Deeds of the Bishops of England, (The Boydell Press, 2002), pp115–16
[viii] Ibid., p.202
[ix] Sawyer, P.H. (ed.), Anglo-Saxon charters: An annotated list and bibliography, rev. Kelly, S.E., Rushforth, R., (2022). http://www.esawyer.org.uk/ S446
You can read about the many daughters of Edward the Elder in The King’s Daughter.
My first non-fiction title, The Royal Women Who Made England, is also now available in ebook and hardback and features these women and what we know about them.